STEAM approach in project-based learning to develop mathematical literacy and students' character
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
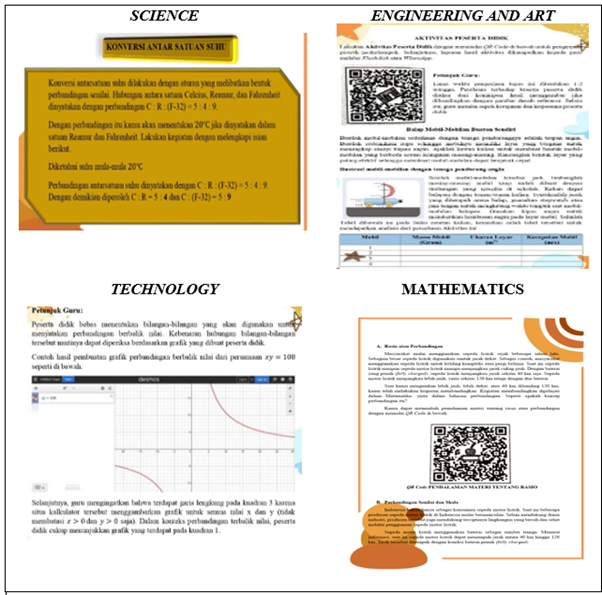
Mathematics is essential for individuals to solve everyday life problems. However, students remain insufficiently motivated in mathematics learning, necessitating the implementation of engaging teaching approaches integrated with other disciplines, such as STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics). This study investigated the effectiveness of a STEAM-based Project-Based Learning (PjBL) approach on mathematical literacy and character development among secondary school students. Utilizing a mixed-methods convergent parallel design, the research employed quantitative and qualitative techniques. The quantitative data collection used a literacy skills test to measure mathematical literacy. Meanwhile, the qualitative data collection to measure students' character utilized surveys, interviews, and observations. Quantitative data analysis was conducted using the Kruskal-Wallis test, while qualitative data analysis employed triangulation, including data reduction, data presentation, and data verification stages. The study results revealed that students' mathematical literacy significantly improved after participating in STEAM-PjBL-based learning. Additionally, STEAM-PjBL fosters the development of students' character traits, including teamwork, communication, and responsibility, highlighting its potential to support holistic educational outcomes. These findings indicate that integrating STEAM principles with PjBL enhances academic performance and cultivates critical 21st-century skills.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Aguilera, D., & Ortiz-Revilla, J. (2021). STEM vs. STEAM education and student creativity: A systematic literature review. Education Sciences, 11(7), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11070331
Ahmad, D. N., Astriani, M. M., Alfahnum, M., & Setyowati, L. (2021). Increasing creative thinking of students by learning organization with steam education. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 10(1), 103-110. https://doi.org/10.15294/jpii.v10i1.27146
Akman, E., & Çakır, R. (2023). The effect of educational virtual reality game on primary school students’ achievement and engagement in mathematics. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(3), 1467-1484. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1841800
Albeshree, F., Al-Manasia, M., Lemckert, C., Liu, S., & Tran, D. (2022). Mathematics teaching pedagogies to tertiary engineering and information technology students: a literature review. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 53(6), 1609-1628. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1837399
Aleksić, G., Merrell, C., Ferring, D., Tymms, P., & Klemenović, J. (2019). Links between socio-emotional skills, behavior, mathematics and literacy performance of preschool children in Serbia. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 34(2), 417-438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-018-0387-8
Alwiyah, D., & Imaniyati, N. (2018). Keterampilan mengajar guru dan kesiapan belajar siswa sebagai determinan terhadap hasil belajar siswa [Teacher teaching skills and student learning readiness as determinants of student learning outcomes]. Jurnal Manajerial, 17(1), 95-103. https://doi.org/10.17509/manajerial.v17i1.9767
Andriyani, A., Santosa, A. B., & Saryadi, W. (2022). Effectiveness of Microsoft Kaizala and Google Classroom towards students’ mathematical communication skill and self-efficacy in learning statistics. Bulletin of Applied Mathematics and Mathematics Education, 2(1), 33-46. https://doi.org/10.12928/bamme.v2i1.5523
Angraini, G., & Sriyati, S. (2019). Analisis kemampuan berpikir tingkat tinggi siswa SMAN Kelas X di kota Solok pada konten biologi [Analysis of high-level thinking skills of grade X senior high school students in Solok city on biology content]. Journal of Education Informatic Technology and Science (JeITS), 1(1), 114-124.
Bai, B., & Wang, J. (2023). The role of growth mindset, self-efficacy and intrinsic value in self-regulated learning and English language learning achievements. Language Teaching Research, 27(1), 207-228. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362168820933190
Başaran, M., & Bay, E. (2023). The effect of project-based STEAM activities on the social and cognitive skills of preschool children. Early Child Development and Care, 193(5), 679-697. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2022.2146682
Becker, K. H., & Park, K. (2011). Integrative approaches among science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects on students’ learning: A meta-analysis. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and Research, 12(5), 23-37.
Bertrand, M. G., & Namukasa, I. K. (2020). STEAM education: student learning and transferable skills. Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, 13(1), 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIT-01-2020-0003
Boice, K. L., Jackson, J. R., Alemdar, M., Rao, A. E., Grossman, S., & Usselman, M. (2021). Supporting teachers on their STEAM journey: A collaborative STEAM teacher training program. Education Sciences, 11(3), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11030105
Cai, J. (2023). Evaluation of blended teaching in STEAM education using structural equation model questionnaire technology. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 18(19), 72-83. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v18i19.43873
Chang, C.-Y., Du, Z., Kuo, H.-C., & Chang, C.-C. (2023). Investigating the impact of design thinking-based STEAM PBL on students’ creativity and computational thinking. IEEE Transactions on Education, 66(6), 673-681. https://doi.org/10.1109/TE.2023.3297221
Chen, C.-C., & Huang, P.-H. (2023). The effects of STEAM-based mobile learning on learning achievement and cognitive load. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(1), 100-116. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1761838
Chen, R. H. (2021). Fostering students’ workplace communicative competence and collaborative mindset through an inquiry-based learning design. Education Sciences, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11010017
Chistyakov, A. A., Zhdanov, S. P., Avdeeva, E. L., Dyadichenko, E. A., Kunitsyna, M. L., & Yagudina, R. I. (2023). Exploring the characteristics and effectiveness of project-based learning for science and STEAM education. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 19(5), em2256. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13128
Conradty, C., & Bogner, F. X. (2020). STEAM teaching professional development works: effects on students’ creativity and motivation. Smart learning environments, 7(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-020-00132-9
Cunha, M. N., Figueiredo, J., Oliveira, I., & Maçães, M. (2024). Motivating students for success: A review of new projects in teaching based on STEM education. Economics: Time Realities, 71(1), 65-71. https://doi.org/10.15276/ETR.01.2024.8
Diego-Mantecon, J.-M., Prodromou, T., Lavicza, Z., Blanco, T. F., & Ortiz-Laso, Z. (2021). An attempt to evaluate STEAM project-based instruction from a school mathematics perspective. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(5), 1137-1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01303-9
Dostál, J., Děrda, R., Částková, P., Mrázek, M., Kubrický, J., Steingartner, W., Bučková, H., Janu, M., & Kronáč, J. (2022). Innovative Concept of STEAM Education at Primary Schools in the Czech Republic-Support for Implementation in School Practice. In 2022 IEEE 16th International Scientific Conference on Informatics (Informatics), Poprad, Slovakia (pp. 60-66). https://doi.org/10.1109/Informatics57926.2022.10083467
Duo-Terron, P., Hinojo-Lucena, F.-J., Moreno-Guerrero, A.-J., & López-Núñez, J.-A. (2022). STEAM in primary education. impact on linguistic and mathematical competences in a disadvantaged context. Frontiers in Education, 7, 792656. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.792656
Effendi, K. N. S., Zulkardi, Z., Putri, R. I. I., & Yaniawati, P. (2020). Reading text for school literacy movement in mathematics learning. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 145-154. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.6731.145-154
Fauzan, A., Harisman, Y., Yerizon, Y., Suherman, S., Tasman, F., Nisa, S., Sumarwati, S., Hafizatunnisa, H., & Syaputra, H. (2024). Realistic mathematics education (RME) to improve literacy and numeracy skills of elementary school students based on teachers’ experience. Infinity Journal, 13(2), 301-316. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i2.p301-316
Fisher, D., Yaniawati, P., & Kusumah, Y. S. (2017). The use of CORE model by metacognitive skill approach in developing characters junior high school students. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1868(1), 050010. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995137
Gabriel, F., Buckley, S., & Barthakur, A. (2020). The impact of mathematics anxiety on self-regulated learning and mathematical literacy. Australian Journal of Education, 64(3), 227-242. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004944120947881
Gellert, U., Jablonka, E., & Keitel, C. (2013). Mathematical literacy and common sense in mathematics education. In B. Atweh, H. Forgasz, & B. Nebres (Eds.), Sociocultural research on mathematics education (pp. 57-73). Routledge.
Hadiyanti, N. F. D., Hobri, H., Prihandoko, A. C., Susanto, S., Murtikusuma, R. P., Khasanah, N., & Maharani, P. (2021). Development of mathematics e-module with STEM-collaborative project based learning to improve mathematical literacy ability of vocational high school students. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1839(1), 012031. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1839/1/012031
Hardman, J. (2019). Towards a pedagogical model of teaching with ICTs for mathematics attainment in primary school: A review of studies 2008-2018. Heliyon, 5(5), e01726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01726
Harisman, Y., Noto, M. S., & Hidayat, W. (2021). Investigation of students' behavior in mathematical problem solving. Infinity Journal, 10(2), 235-258. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v10i2.p235-258
Herrero, A. C., Recio, T., Tolmos, P., & Vélez, M. P. (2023). From the STEAM engine to STEAM education: An experience with pre-service mathematics teachers. Mathematics, 11(2), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020473
Herro, D., Quigley, C., Plank, H., Abimbade, O., & Owens, A. (2022). Instructional practices promoting computational thinking in STEAM elementary classrooms. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 38(4), 158-172. https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2022.2087125
Hsiao, P.-W., & Su, C.-H. (2021). A study on the impact of STEAM education for sustainable development courses and its effects on student motivation and learning. Sustainability, 13(7), 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073772
Hsu, Y.-C. (2020). Exploring the learning motivation and effectiveness of applying virtual reality to high school mathematics. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(2), 438-444. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080214
Indahwati, S. D., Rachmadiarti, F., & Hariyono, E. (2023). Integration of PJBL, STEAM, and learning tool development in improving students' critical thinking skills. IJORER: International Journal of Recent Educational Research, 4(6), 808-818. https://doi.org/10.46245/ijorer.v4i6.434
Ishartono, N., Razak, R. b. A., Kholid, M. N., Arlinwibowo, J., & Afiyah, A. N. (2024). Integrating STEAM into flip flop model to improve students’ understanding on composition of functions during online learning. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 45-60. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p45-60
Iyer, V., Naandheny, S., & Manjuri, D. (2023). A Review of Pedagogical Advancements in Mathematics Education for Future Engineers. In 2023 2nd International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), Coimbatore, India (pp. 1-6). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAECA56562.2023.10200980
Jesionkowska, J., Wild, F., & Deval, Y. (2020). Active learning augmented reality for STEAM education—A case study. Education Sciences, 10(8), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10080198
Kadir, D., Judijanto, L., Widodo, J., Sidik, E. A., Haq, M. S., & Santosa, T. A. (2023). The effect STEAM based discovery learning model on students thinking ability: Meta-analysis study. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA, 9(12), 1245-1253. https://doi.org/10.29303/jppipa.v9i12.5944
Kariadinata, R., Yaniawati, R. P., Juariah, J., Sugilar, H., & Muthmainah, A. (2019). Spatial thinking ability and mathematical character students through Cabri 3D with a scientific approach. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1402(7), 077094. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1402/7/077094
Khairani, C. P., & Mudjiran, M. (2022). Pengembangan modul bimbingan dan konseling untuk meningkatkan karakter tangguh siswa dalam belajar [Development of guidance and counseling modules to improve students' resilient character in learning]. Jurnal Riset Tindakan Indonesia, 7(4), 642-650.
Kim, Y. E., Morton, B. G., Gregorio, J., Rosen, D. S., Edouard, K., & Vallett, R. (2019). Enabling creative collaboration for all levels of learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(6), 1878-1885. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1808678115
Körtesi, P., Simonka, Z., Szabo, Z. K., Guncaga, J., & Neag, R. (2022). Challenging examples of the wise use of computer tools for the sustainability of knowledge and developing active and innovative methods in STEAM and mathematics education. Sustainability, 14(20), 12991. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142012991
Kozakli Ulger, T., Bozkurt, I., & Altun, M. (2022). Analyzing in-service teachers' process of mathematical literacy problem posing. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 17(3), em0687. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/11985
Kurniawati, R. P., Gunawan, I., & Marlina, D. (2020). Mathematic literation abilities based on problem solving abilities in first class 4 of elementary school. In 2nd Early Childhood and Primary Childhood Education (ECPE 2020), (pp. 186-192). https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.201112.033
Li, J., Luo, H., Zhao, L., Zhu, M., Ma, L., & Liao, X. (2022). Promoting STEAM education in primary school through cooperative teaching: A design-based research study. Sustainability, 14(16), 10333. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610333
Lin, C.-L., & Tsai, C.-Y. (2021). The effect of a pedagogical STEAM model on students’ project competence and learning motivation. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 30(1), 112-124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-020-09885-x
Mahlow, C., & Hediger, A. (2021). Education as loosely coupled system of technology and pedagogy. On Education: Journal for Research and Debate, 4(12), 1-11.
Murtiyasa, B., & Perwita, W. R. G. (2020). Analysis of mathematics literation ability of students in completing PISA-oriented mathematics problems with changes and relationships content. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(7), 3160-3172. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080745
Nantschev, R., Feuerstein, E., González, R. T., Alonso, I. G., Hackl, W. O., Petridis, K., Triantafyllou, E., & Ammenwerth, E. (2020). Teaching approaches and educational technologies in teaching mathematics in higher education. Education Sciences, 10(12), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10120354
Ng, A. (2024). Empowering Malaysian early childhood practitioners’ sustainable inclusive practices through the ‘integrating and navigating Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics’(inSTEAM) framework. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 20(11), em2531. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/15579
Ní Shé, C., Ní Fhloinn, E., & Mac an Bhaird, C. (2023). Student engagement with technology-enhanced resources in mathematics in higher education: A review. Mathematics, 11(3), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11030787
Novita, R., & Herman, T. (2021). Digital technology in learning mathematical literacy, can it helpful? Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1776(1), 012027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1776/1/012027
Ozkan, G., & Umdu Topsakal, U. (2021). Investigating the effectiveness of STEAM education on students’ conceptual understanding of force and energy topics. Research in Science & Technological Education, 39(4), 441-460. https://doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2020.1769586
Pellegrini, M., Lake, C., Neitzel, A., & Slavin, R. E. (2021). Effective programs in elementary mathematics: A meta-analysis. AERA Open, 7(1), 1-29. https://doi.org/10.1177/2332858420986211
Putri, A. S., Prasetyo, Z. K., Purwastuti, L. A., Prodjosantoso, A. K., & Putranta, H. (2023). Effectiveness of STEAM-based blended learning on students’ critical and creative thinking skills. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 12(1), 44-52. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v12i1.22506
Quigley, C. F., Herro, D., Shekell, C., Cian, H., & Jacques, L. (2020). Connected learning in STEAM classrooms: opportunities for engaging youth in science and math classrooms. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 18(8), 1441-1463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-10034-z
Rahmawati, Y., Taylor, E., Taylor, P. C., Ridwan, A., & Mardiah, A. (2022). Students’ engagement in education as sustainability: Implementing an ethical dilemma-STEAM teaching model in chemistry learning. Sustainability, 14(6), 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063554
Rodríguez-Nieto, C. A., & Alsina, Á. (2022). Networking between ethnomathematics, STEAM education, and the globalized approach to analyze mathematical connections in daily practices. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics Science and Technology Education, 18(3), em2085. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/11710
Setiawati, S., Herman, T., & Jupri, A. (2017). Investigating middle school students’ difficulties in mathematical literacy problems level 1 and 2. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 909(1), 012063. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/909/1/012063
Shi, A., Wang, Y., & Ding, N. (2022). The effect of game–based immersive virtual reality learning environment on learning outcomes: designing an intrinsic integrated educational game for pre–class learning. Interactive Learning Environments, 30(4), 721-734. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1681467
Silawati, E. (2019). New media literacy in the context of early childhood education (An overview from Indonesian kindergarten future teachers). In International Conference on Education, Social Sciences and Humanities, (pp. 12-16).
Siregar, Y. E. Y., Rahmawati, Y., & Suyono, S. (2023). The impact of an integrated STEAM project delivered via mobile technology on the reasoning ability of elementary school students. JOTSE: Journal of Technology and Science Education, 13(1), 410-428. https://doi.org/10.3926/jotse.1446
Stacey, K. (2015). The international assessment of mathematical literacy: PISA 2012 framework and items. In S. J. Cho (Ed.), Selected Regular Lectures from the 12th International Congress on Mathematical Education (pp. 771-790). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17187-6_43
Suganda, E., Latifah, S., Irwandani, Sari, P. M., Rahmayanti, H., Ichsan, I. Z., & Mehadi Rahman, M. (2021). STEAM and Environment on students’ creative-thinking skills: A meta-analysis study. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1796(1), 012101. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1796/1/012101
Sukmawati, E., Imanah, N. D. N., & Rantauni, D. A. (2023). Implementation and challenges of project-based learning of STEAM in the university during the pandemic: A systematic literature review. JINoP (Jurnal Inovasi Pembelajaran), 9(1), 128-139. https://doi.org/10.22219/jinop.v9i1.25177
Supianti, I. I., Yaniawati, P., Osman, S. Z. M., Al-Tamar, J., & Lestari, N. (2022). Development of teaching materials for e-learning-based statistics materials oriented towards the mathematical literacy ability of vocational high school students. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 237-254. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p237-254
Umbara, U., Prabawanto, S., & Jatisunda, M. G. (2023). Combination of mathematical literacy with ethnomathematics: How to perspective sundanese culture. Infinity Journal, 12(2), 393-414. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i2.p393-414
Wahba, F. A.-A., Tabieh, A. A., & Banat, S. Y. (2022). The power of STEAM activities in enhancing the level of metacognitive awareness of mathematics among students at the primary stage. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(11), em2185. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12562
Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
Witdiya, T., Supriadi, G., Supriatin, A., & Annovasho, J. (2023). The effect of STEAM learning on improving each indicator of students’ creative thinking in physics learning. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Fisika, 7(1), 42-50. https://doi.org/10.20527/jipf.v7i1.7158
Yaniawati, P., Fisher, D., Permadi, Y. D., & Yatim, S. A. M. (2023). Development of mobile-based digital learning materials in blended learning oriented to students’ mathematical literacy. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 13(9), 1338-1347. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2023.13.9.1936
Yaniawati, P., & Indrawan, R. (2024). Metode penelitian: Konsep, teknik, dan aplikasi [Research methods: Concepts, techniques and applications]. Refika Aditama.
Yeager, D. S., & Dweck, C. S. (2020). What can be learned from growth mindset controversies? American psychologist, 75(9), 1269-1284. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000794
Yeager, D. S., Hanselman, P., Walton, G. M., Murray, J. S., Crosnoe, R., Muller, C., Tipton, E., Schneider, B., Hulleman, C. S., Hinojosa, C. P., Paunesku, D., Romero, C., Flint, K., Roberts, A., Trott, J., Iachan, R., Buontempo, J., Yang, S. M., Carvalho, C. M., . . . Dweck, C. S. (2019). A national experiment reveals where a growth mindset improves achievement. Nature, 573(7774), 364-369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1466-y
Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Leong, C., Mao, Y., & Yuan, Z. (2024). Bridging stories and science: An fNIRS-based hyperscanning investigation into child learning in STEM. NeuroImage, 285, 120486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120486
Ziatdinov, R., & Valles, J. R. (2022). Synthesis of modeling, visualization, and programming in GeoGebra as an effective approach for teaching and learning STEM topics. Mathematics, 10(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10030398