Main Article Content
Abstract
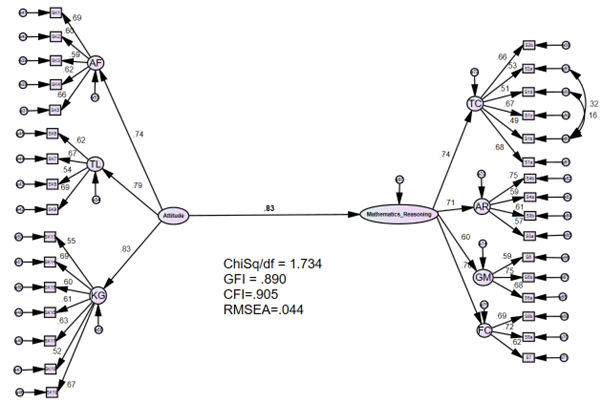
Studies on mathematics achievement status show that mathematical reasoning in Malaysian education is critical, especially among university students. Students' attitude toward mathematics is affected by affective, behavioural and cognitive factors. The present research investigated the connections between these variables and their impact on individuals' attitudes towards mathematics reasoning. A statistical analysis method, namely, AMOS-Structural Equation Modelling, was used in this approach. The survey method involving 378 university education students around the Klang Valley was selected using a proportional stratified random sampling technique. The respondents must complete the mathematics reasoning assessment and answer the questionnaire consisting of three components: affective, behavioural and cognitive towards mathematics reasoning. AMOS-Structural Equation Modelling (AMOS-SEM) was applied using data obtained from questionnaires. Results demonstrated that the measurement models showed acceptable validity and reliability by removing some indications from the scales. The findings illustrate the relationship between students' attitudes and mathematical reasoning. Moreover, attitude is significantly related to students' mathematical reasoning performance in university education. The next study's recommendation involves an interview session to explore more findings that might impact their learning in mathematical reasoning.
Keywords
AMOS-SEM
Attitude towards mathematics
Mathematics reasoning
Undergraduate
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
- Ahmadah, I. F. (2020). Algebraic reasoning of student with Keirsey personality type in solving mathematical problem. Eduma : Mathematics Education Learning and Teaching, 9(2), 42-48. https://doi.org/10.24235/eduma.v9i2.7191
- Aisyah, N., Susanti, E., Meryansumayeka, M., Siswono, T. Y. E., & Maat, S. M. (2023). Proving geometry theorems: Student prospective teachers' perseverance and mathematical reasoning. Infinity Journal, 12(2), 377-392. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i2.p377-392
- Ajisuksmo, C. R. P., & Saputri, G. R. (2017). The influence of attitudes towards mathematics, and metacognitive awareness on mathematics achievements. Creative Education, 8(3), 486-497. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2017.83037
- Alibraheim, E. A. (2021). Factors affecting freshman engineering students' attitudes toward mathematics. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 17(6), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/10899
- Awang, Z. (2018). A handbook on structural equation modeling using AMOS. Universiti Teknologi MARA Publication.
- Bakar, S. A., & Ayub, A. F. M. (2020). Relationship between attitude towards mathematics and mathematical problem-solving achievement among pre-university students in Malaysia. ASM Science Journal, 13, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.32802/ASMSCJ.2020.SM26(2.24)
- Boonsathirakul, J., & Kerdsomboon, C. (2021). The investigation of critical thinking disposition among Kasetsart university students. Higher Education Studies, 11(2), 224-232. https://doi.org/10.5539/hes.v11n2p224
- Campos-Fabian, D. R. (2020). Pensamiento crítico y el aprendizaje de la matemática en estudiantes ingresantes a la universidad [Critical thinking and learning of mathematics in incoming college students]. Eduser, 7(2), 82-94. https://doi.org/10.18050/eduser.v7i2.2538
- Ceballos-Bejarano, F., Pacheco-Quico, M., Mamani-Daza, L., Ceballos-Bejarano, E., Huaita-Bedregal, A., Ortiz-Cansaya, S., Condori-Mamani, H., Aguilar-Pinto, U., & Tejada-Franco, S. V. (2023). Attitudes towards mathematics in undergraduate students of accounting and administrative sciences in Peru. Journal of Higher Education Theory and Practice, 23(12), 88-96. https://doi.org/10.33423/jhetp.v23i12.6240
- Ching, G. S., Hu, Y. L., & Roberts, A. (2021). The part and parcel of doctoral education: A gap analysis between the importance and satisfaction of the experience. Education Sciences, 11(9), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090481
- Cresswell, C., & Speelman, C. P. (2020). Does mathematics training lead to better logical thinking and reasoning? A cross-sectional assessment from students to professors. PLoS One, 15(7), e0236153. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236153
- Di Martino, P., & Zan, R. (2011). Attitude towards mathematics: a bridge between beliefs and emotions. Zdm, 43(4), 471-482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-011-0309-6
- Din, M. (2020). Evaluating university students’ critical thinking ability as reflected in their critical reading skill: A study at bachelor level in Pakistan. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 35, 100627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100627
- Elçi, A. N. (2017). Students’ attitudes towards mathematics and the impacts of mathematics teachers’ approaches on it. Acta Didactica Napocensia, 10(2), 99-108. https://doi.org/10.24193/adn.10.2.8
- Eriksson, H., & Sumpter, L. (2021). Algebraic and fractional thinking in collective mathematical reasoning. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 108(3), 473-491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-021-10044-1
- Fennema, E., & Sherman, J. A. (1976). Brief reports: Fennema-Sherman mathematics attitudes scales: Instruments designed to measure attitudes toward the learning of mathematics by females and males. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education JRME, 7(5), 324-326. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.7.5.0324
- Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39-50. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312
- Franke, G., & Sarstedt, M. (2019). Heuristics versus statistics in discriminant validity testing: a comparison of four procedures. Internet Research, 29(3), 430-447. https://doi.org/10.1108/IntR-12-2017-0515
- Haeruman, L. D., Salsabila, E., & Kharis, S. A. A. (2024). The impact of mathematical reasoning and critical thinking skills on mathematical literacy skills. KnE Social Sciences, 542-550. https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v9i13.15957
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2019). Multivariate data analysis International Statistical Review / Revue Internationale de Statistique,
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
- Indraswari, N. F., Budayasa, I. K., & Ekawati, R. (2018). Algebraic reasoning in solving mathematical problem based on learning style. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 947(1), 012061. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/947/1/012061
- Kovács, E., & Maričić, S. (2023). Stavovi učenika prema matematici kao element motivacije za učenje u nižim razredima [Students' attitudes towards mathematics in lower grades as an element of motivation for learning]. Zbornik radova Pedagoskog fakulteta Uzice(25), 77-96. https://doi.org/10.5937/zrpfu2325077k
- Layco, E. P., & Parico, A. D. (2019). Self-regulated learning straegies and mathematics achievement : the mediating influences of students attitude towards mathematics, deferred gratification, and engagement in mathematics. Journal of Mechanics of Continua and Mathematical Sciences(4), 222-230. https://doi.org/10.26782/jmcms.spl.4/2019.11.00022
- Livy, S., & Herbert, S. (2013). Second-year pre-service teachers' responses to proportional reasoning test items. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 38(11), 17-32. https://doi.org/10.14221/ajte.2013v38n11.7
- Marhami, M., Rohantizani, R., & Nuraina, N. (2020). Improving students’ critical mathematical thinking skills through SAVI approach on number theory lectures at mathematics education department of Malikussaleh university. International Journal for Educational and Vocational Studies, 2(1), 9-13. https://doi.org/10.29103/ijevs.v2i1.2020
- Mueller, R. O., & Hancock, G. R. (2018). Structural equation modeling. In G. R. Hancock, L. M. Stapleton, & R. O. Mueller (Eds.), The Reviewer’s Guide to Quantitative Methods in the Social Sciences (2nd ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315755649-33
- Núñez-Peña, M. I., Suárez-Pellicioni, M., & Bono, R. (2013). Effects of math anxiety on student success in higher education. International Journal of Educational Research, 58, 36-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2012.12.004
- Radmehr, F., Nedaei, M., & Drake, M. (2020). Exploring undergraduate engineering students' competencies and attitudes towards mathematical problem-posing in integral calculus In INDRUM 2020, Cyberspace (virtually from Bizerte), Tunisia. https://hal.science/hal-03113968
- Ragudo, J. M. G. (2024). Logical thinking skills and problem solving skills of the grade 12 STEM students of university of Northern Philippines: A basis for extension plan. International Journal of Research Studies in Education, 13(6), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.5861/ijrse.2024.23077
- Ramazan, A., & Seher, A. (2015). Turkish adaptation of utley geometry attitude scale: A validity and reliability study. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research(58), 1-23.
- Risnawati, R., Andrian, D., Azmi, M. P., Amir, Z., & Nurdin, E. (2019). Development of a definition maps-based plane geometry module to improve the student teachers' mathematical reasoning ability. International Journal of Instruction, 12(3), 541-560. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2019.12333a
- Rozgonjuk, D., Kraav, T., Mikkor, K., Orav-Puurand, K., & Täht, K. (2020). Mathematics anxiety among STEM and social sciences students: the roles of mathematics self-efficacy, and deep and surface approach to learning. International journal of STEM education, 7(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00246-z
- Satiti, W. S., & Wulandari, K. (2021). Students' ability to think mathematically in solving PISA mathematics problems content change and relationship. Mathematics Education Journal, 5(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.22219/mej.v5i1.14380
- Shakya, S., & Maharjan, R. (2023). Students’ attitude towards mathematics and its relationship with mathematics achievement. Mangal Research Journal, 4(1), 29-40. https://doi.org/10.3126/mrj.v4i01.61718
- Singh, P., Hoon, T. S., Nasir, N. A. M., Han, C. T., Rasid, N. S. M., & Bzh, J. (2020). An analysis of students' mathematical reasoning and mental computation proficiencies. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(11), 5628-5636. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.081167
- Svenningsson, J., Höst, G., Hultén, M., & Hallström, J. (2022). Students’ attitudes toward technology: exploring the relationship among affective, cognitive and behavioral components of the attitude construct. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 32(3), 1531-1551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-021-09657-7
- Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2019). Using multivariate statistics (7th ed.). Pearson. https://lccn.loc.gov/2017040173
- Tak, C. C., Hutkemri, H., & Eu, L. K. (2021). Analysis validity and reliability of self-efficacy and metacognitive awareness instrument toward mathematical reasoning. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(9), 3332-3344. https://doi.org/10.17762/turcomat.v12i9.5739
- Tak, C. C., Zulnaidi, H., & Eu, L. K. (2022). Measurement model testing: Adaption of self-efficacy and metacognitive awareness among university students. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(9), em2153. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12366
- Takele, K., Zewotir, T., & Ndanguza, D. (2023). A combined model of child malnutrition and morbidity in Ethiopia using structural equation models. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-27440-7
- Tapia, M., & Marsh, G. E. (2004). An instrument to measure mathematics attitudes. Academic Exchange Quarterly, 8(2), 16-22.
- Teo, T. (2013). Handbook of quantitative methods for educational research. SensePublishers Rotterdam. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-6209-404-8
- Ullman, J. B., & Bentler, P. M. (2012). Structural equation modeling. In I. Weiner, J. A. Schinka, & W. F. Velicer (Eds.), Handbook of Psychology, Second Edition (pp. 661-690). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118133880.hop202023
- Verma, J. P., & Verma, P. (2024). Understanding Structural Equation Modeling: A Manual for Researchers. Springer Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-32673-8
- Vlasenko, K., Achkan, V., Chumak, O., Lovianova, I., & Armash, T. (2020). Problem-based approach to develop creative thinking in students majoring in mathematics at teacher training universities. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 8(7), 2853-2863. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2020.080712
- Wagner, W. E., III. (2019). Using IBM SPSS statistics for research methods and social science statistics (7th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Wahyuni, Y., & Jamaris, J. (2021). Analysis of students' mathematical reasoning ability with the constructivism approach through mobile learning system. Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies, 24(1), 55-60.
- Wijaya, T. T., Cao, Y., Bernard, M., Rahmadi, I. F., Lavicza, Z., & Surjono, H. D. (2022). Factors influencing microgame adoption among secondary school mathematics teachers supported by structural equation modelling-based research. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.952549
- Wijaya, T. T., Cao, Y., Weinhandl, R., Yusron, E., & Lavicza, Z. (2022). Applying the UTAUT Model to Understand Factors Affecting Micro-Lecture Usage by Mathematics Teachers in China. Mathematics, 10(7), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10071008
- Zanabazar, A., Deleg, A., Ravdan, M., & Tsogt-Erdene, E. (2023). The relationship between mathematics anxiety and mathematical performance among undergraduate students. Jurnal Ilmiah Peuradeun, 11(1), 309-322. https://doi.org/10.26811/peuradeun.v11i1.780