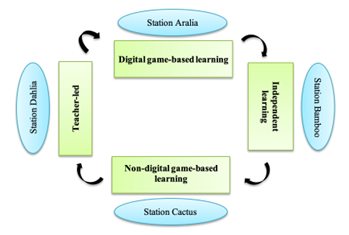
Mastering fractions and innovating with the station rotation model in blended learning
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
This study explores the effectiveness of the Station Rotation Model (SRM) in adding and subtracting fractions. A mixed-method design was conducted through convenience sampling of 31 students from Year 9. They were given pre-and post-tests consisting of ten questions for collecting quantitative data. Students’ online questionnaires consisting of five-point Likert scales, two open-ended questions, and structured interviews with six selected students were further analysed to collect qualitative data. A non-parametric test was adopted to compare the results of the achievement tests. Wilcoxon’s signed rank test findings showed a significant difference (p=0.024) and a large effect size (rb=0.558) between the achievement test scores. This indicates that the SRM positively impacts students’ performance in adding and subtracting fractions. Three major themes emerged from the questionnaires and interviews about students’ perception of using SRM: Manipulatives make learning fun, enjoyment of working in a group, and challenges in implementing the SRM. Overall, students positively viewed their experiences with the SRM as an approach to teaching and learning. The study offers insights into SRM’s impact on student learning, aiding educators amd researchers assess its future application, especially in mathematics education.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Abbas, N. A., Abdullah, N. A., Shahrill, M., & Tengah, K. A. (2022). Primary school pupils’ performance on the addition of fractions: Conceptual and procedural knowledge. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(2), 227-238. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.2.17811.227-238
Abbas, N. A. H., Shahrill, M., & Indra Prahmana, R. C. (2020). Understanding primary school children’s learning on addition of fractions. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1613(1), 012046. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1613/1/012046
Akinoso, S. O., Agoro, A. A., & Alabi, O. M. (2020). Effect of station rotation mode of instructional delivery for mathematics in the era of advancing technology. Journal of the International Society for Teacher Education, 24(2), 60-72.
Ali, H. A. H., Salleh, S. M., & Shahrill, M. (2015). Technology integration in the context of Brunei primary schools. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 14(2), 558-568.
Ali, H. M. H. H. M., Asamoah, D., & Shahrill, M. (2022). Effectiveness of flipped classroom model through multimedia technology in improving students' performance in directed numbers. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 193-210. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p193-210
Almahasees, Z., Mohsen, K., & Amin, M. O. (2021). Faculty’s and students’ perceptions of online learning during COVID-19. Frontiers in Education, 6, 638470. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.638470
Anthony Jnr, B. (2022). An exploratory study on academic staff perception towards blended learning in higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 27(3), 3107-3133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10705-x
Ayob, N. F. S., Halim, N. D. A., Zulkifli, N. N., Zaid, N. M., & Mokhtar, M. (2020). Overview of blended learning: The effect of station rotation model on students’ achievement. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(6), 320-326.
Bayeck, R. Y. (2020). Examining board gameplay and learning: A multidisciplinary review of recent research. Simulation & Gaming, 51(4), 411-431. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878119901286
Belazi, N., & Ganapathy, M. (2021). The effects of the station rotation model in promoting Libyan students’ EFL writing: Blended learning. AJELP: Asian Journal of English Language and Pedagogy, 9(1), 111-127.
Belazi, N. A., & Ganapathy, M. (2023). Teachers’ and students’ perceptions towards the station rotation model: A case of Libyan EFL writing classroom. AJELP: Asian Journal of English Language and Pedagogy, 11(1), 22-36.
Bhardwaj, R., Jafri, S., Mohan, D., Upreti, K., Kumar, N., & Sharma, V. (2022, 22-24 June 2022). Role of e-learning in educational institutions: Analyzing its impact on students’ satisfaction and performance In 2022 7th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), (pp. 1667-1678). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCES54183.2022.9835746
Bouck, E. C., & Long, H. (2023). Online delivery of a manipulative-based intervention package for finding equivalent fractions. Journal of Behavioral Education, 32(2), 313-333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09449-y
Bower, M., Dalgarno, B., Kennedy, G. E., Lee, M. J. W., & Kenney, J. (2015). Design and implementation factors in blended synchronous learning environments: Outcomes from a cross-case analysis. Computers & Education, 86, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.03.006
Chaeruman, U. A., Wibawa, B., & Syahrial, Z. (2018). Determining the appropriate blend of blended learning: A formative research in the context of spada-Indonesia. American Journal of Educational Research, 6(3), 188-195. https://doi.org/10.12691/education-6-3-5
Cooper, J. L., Sidney, P. G., & Alibali, M. W. (2018). Who benefits from diagrams and illustrations in math problems? Ability and attitudes matter. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 32(1), 24-38. https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.3371
Creswell, J. W., Clark, V. L. P., Gutmann, M. L., & Hanson, W. E. (2003). Advanced mixed methods research designs. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social and behavioral research (pp. 209–240). Sage.
Delucchi, M. (2014). Measuring student learning in social statistics: A pretest-posttest study of knowledge gain. Teaching Sociology, 42(3), 231-239. https://doi.org/10.1177/0092055x14527909
Faradillah, A., & Hadi, W. (2020). Educators’ perception of blended learning models on mathematics learning. Kalamatika: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 5(1), 83-92. https://doi.org/10.22236/KALAMATIKA.vol5no1.2020pp83-92
Finti, H. N. F. M. M., Shahrill, M., & Salleh, S. M. (2016). Integrating virtual manipulative with the use of iPad in the teaching and learning of fractions. Knowledge Management & E-Learning, 8(4), 581-601. https://doi.org/10.34105/j.kmel.2016.08.036
Fitri, S., & Zahari, C. L. (2019). The implementation of blended learning to improve understanding of mathematics. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1188(1), 012109. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1188/1/012109
Fox, S., & Mackeogh, K. (2003). Can elearning promote higher-order learning without tutor overload? Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and e-Learning, 18(2), 121-134. https://doi.org/10.1080/02680510307410
Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning: Uncovering its transformative potential in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 7(2), 95-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2004.02.001
George‐Walker, L. D., & Keeffe, M. (2010). Self‐determined blended learning: a case study of blended learning design. Higher Education Research & Development, 29(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360903277380
Gerald, B. (2018). A brief review of independent, dependent and one sample t-test. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, 4(2), 50-54. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijamtp.20180402.13
Gobbo, E. d., Guarino, A., Cafarelli, B., Grilli, L., & Limone, P. (2022). On the perceptions of online learning due to COVID-19 pandemic. Case study: University of Foggia, Italy In P. Limone, R. Di Fuccio, & G. A. Toto, In Psychology, Learning, Technology, Cham (pp. 130-149). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15845-2_9
Govindaraj, A., & Silverajah, V. S. G. (2017). Blending flipped classroom and station rotation models in enhancing students' learning of physics Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Education Technology and Computers, Barcelona, Spain. https://doi.org/10.1145/3175536.3175543
Greener, S. (2021). Exploring remote distance learning: what is it and should we keep it? Interactive Learning Environments, 29(1), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1848506
Halverson, L. R., & Graham, C. R. (2019). Learner engagement in blended learning environments: a conceptual framework. Online Learning, 23(2), 145-178. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v23i2.1481
Hamida, N., Arianto, F., & Hartono, S. (2021). The effect of station rotation online model on problem solving students ability: A case study at junior high school. Review of International Geographical Education Online, 11(10), 1500-1507.
Han, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). System-driven blended learning for quality education: A collective case study of universities and vocational colleges and schools in China. In C. P. Lim & C. R. Graham (Eds.), Blended Learning for Inclusive and Quality Higher Education in Asia (pp. 1-23). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4106-7_1
Hartney, E., Melis, E., Taylor, D., Dickson, G., Tholl, B., Grimes, K., Chan, M.-K., Van Aerde, J., & Horsley, T. (2022). Leading through the first wave of COVID: a Canadian action research study. Leadership in Health Services, 35(1), 30-45. https://doi.org/10.1108/LHS-05-2021-0042
Hidayat, W., & Aripin, U. (2023). How to develop an e-LKPD with a scientific approach to achieving students' mathematical communication abilities? Infinity Journal, 12(1), 85-100. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i1.p85-100
Hidayat, W., Rohaeti, E. E., Hamidah, I., & Putri, R. I. I. (2023). How can android-based trigonometry learning improve the math learning process? Frontiers in Education, 7, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.1101161
Hrastinski, S. (2019). What do we mean by blended learning? TechTrends, 63(5), 564-569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-019-00375-5
Huda, M., Jasmi, K. A., Hehsan, A., Mustari, M. I., Shahrill, M., Basiron, B., & Gassama, S. K. (2017). Empowering children with adaptive technology skills: Careful engagement in the digital ınformation age. International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 9(3), 693-708.
Ismail, N. F. H., Shahrill, M., & Asamoah, D. (2023). Learning through virtual manipulatives: Investigating the impact of Gizmos-based lessons on students’ performance in integers. Contemporary Mathematics and Science Education, 4(1), ep23009. https://doi.org/10.30935/conmaths/12857
Japar, I., Asamoah, D., & Shahrill, M. (2022). Addressing student learning gaps in fractions: How effective is synchronous video conferencing. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 16(1), 103-120. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.16.1.17027.103-120
JASP Team. (2023). JASP (Version 0.17.1) [Computer software]. https://jasp-stats.org
Kaur, A., & Kumar, R. (2015). Comparative analysis of parametric and non-parametric tests. Journal of computer and mathematical sciences, 6(6), 336-342.
Khan, B. (2005). Managing e-learning strategies: Design, delivery, implementation and evaluation. IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-59140-634-1
Kintu, M. J., Zhu, C., & Kagambe, E. (2017). Blended learning effectiveness: The relationship between student characteristics, design features and outcomes. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1), 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0043-4
Kul, Ü., Celik, S., & Aksu, Z. (2018). The impact of educational material use on mathematics achievement: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Instruction, 11(4), 303-324. https://doi.org/10.12973/iji.2018.11420a
Laer, S. V., & Elen, J. (2017). In search of attributes that support self-regulation in blended learning environments. Education and Information Technologies, 22(4), 1395-1454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-016-9505-x
Laidin, D. R., & Tengah, K. A. (2021). Applying butterfly method in the learning of addition and subtraction of fractions. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 15(2), 161-174. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.15.2.13934.161-174
Lastariwati, B., Komariah, K., Mulyatiningsih, E., & Kartika, M. G. (2021). Exploration of the determining factors of successful online learning in the industrial revolution 4.0 era. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1833(1), 012069. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1833/1/012069
Leite, W. L., Kuang, H., Jing, Z., Xing, W., Cavanaugh, C., & Huggins-Manley, A. C. (2022). The relationship between self-regulated student use of a virtual learning environment for algebra and student achievement: An examination of the role of teacher orchestration. Computers & Education, 191, 104615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104615
Lince, R. (2016). Creative thinking ability to increase student mathematical of junior high school by applying models numbered heads together. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(6), 206-212.
Literacy and Numeracy Coaching Programme (LNCP). (2017). Teaching for mathematics mastery framework (CfBT Brunei Education Development Trust, Ed.). Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam.
Low, J., Shahrill, M., & Zakir, N. (2020). Solving fractions by applying the bar model concept with the butterfly method. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 14(2), 101-116. https://doi.org/10.22342/jpm.14.2.11261.101-116
Mahalli, M., Nurkamto, J., Mujiyanto, J., & Yuliasri, I. (2019). The implementation of station rotation and flipped classroom models of blended learning in EFL learning. English Language Teaching, 12(12), 23-29. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v12n12p23
Manjanai, S. N. N. P., & Shahrill, M. (2017). Introducing the flipped classroom strategy in the learning of year nine factorization. The International Journal of Interdisciplinary Educational Studies, 11(4), 35-55. https://doi.org/10.18848/2327-011X/CGP/v11i04/35-55
Matzavela, V., & Alepis, E. (2021). M-learning in the COVID-19 era: Physical vs digital class. Education and Information Technologies, 26(6), 7183-7203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10572-6
McGrath, C., Palmgren, P. J., & Liljedahl, M. (2019). Twelve tips for conducting qualitative research interviews. Medical Teacher, 41(9), 1002-1006. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2018.1497149
Mendiburo, M., & Hasselbring, T. (2014). Technology's impact on fraction learning: An experimental comparison of virtual and physical manipulatives. Journal of Computers in Mathematics and Science Teaching, 33(2), 209-231.
Mendoza, M. J. L., & Lapinid, M. R. C. (2021). Blended learning models in schoology: Effects on students’ mathematics achievements and perception. Intersection, 1(1), 44-52.
Miller, G., & Obara, S. (2017). Finding meaning in mathematical mnemonics. Australian Mathematics Teacher, The, 73(3), 13-18.
Ministry of Education. (2015). Handbook for teacher performance appraisal (2nd ed.). Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam.
Mishra, L., Gupta, T., & Shree, A. (2020). Online teaching-learning in higher education during lockdown period of COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 1, 100012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100012
Moorhouse, B. L., Li, Y., & Walsh, S. (2021). E-classroom interactional competencies: Mediating and assisting language learning during synchronous online lessons. RELC Journal, 54(1), 114-128. https://doi.org/10.1177/0033688220985274
Moorhouse, B. L., & Wong, K. M. (2022). Blending asynchronous and synchronous digital technologies and instructional approaches to facilitate remote learning. Journal of Computers in Education, 9(1), 51-70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-021-00195-8
Nida, N. K., Usodo, B., & Saputro, D. R. S. (2020). The Blended Learning with WhatsApp Media on Mathematics Creative Thinking Skills and Math Anxiety. Journal of Education and Learning (EduLearn), 14(2), 307-314. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v14i2.16233
Nugraha, D. M. D. P. (2020). Station rotation type blended learning model against critical thinking ability of fourth grade students. Journal of Education Technology, 4(4), 516-523. https://doi.org/10.23887/jet.v4i4.29690
Ocak, G. (2010). The effect of learning stations on the level of academic success and retention of elementary school students. New Educational Review, 21(2), 146-156.
Ogude, B. A., & Chukweggu, C. O. (2019). The effects of station rotation model (SRM) and lecture method on blended learning on secondary school students’ performance on reading comprehension. Journal of Advances in Education and Philosophy, 3(10), 376-383. https://doi.org/10.36348/JAEP.2019.v03i10.006
Okagbue, H. I., Oguntunde, P. E., Obasi, E. C. M., & Akhmetshin, E. M. (2021). Trends and usage pattern of SPSS and Minitab Software in Scientific research. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1734(1), 012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1734/1/012017
Ololube, N. P. (2011). Blended learning in Nigeria: Determining students’ readiness and faculty role in advancing technology in a globalized educational development. In A. Kitchenham (Ed.), Blended Learning across Disciplines: Models for Implementation (pp. 190-207). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-60960-479-0.ch011
Orcan, F. (2020). Parametric or non-parametric: Skewness to test normality for mean comparison. International Journal of Assessment Tools in Education, 7(2), 255-265. https://doi.org/10.21449/ijate.656077
Osguthorpe, R. T., & Graham, C. R. (2003). Blended learning environments. Quarterly review of distance education, 4(3), 227.
Ozkan, S., & Koseler, R. (2009). Multi-dimensional students’ evaluation of e-learning systems in the higher education context: An empirical investigation. Computers & Education, 53(4), 1285-1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.06.011
Palioura, M., & Dimoulas, C. (2022). Digital storytelling in education: A transmedia integration approach for the non-developers. Education Sciences, 12(8), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12080559
Parungao, R. C. (2021). Manipulative approach in teaching fractions. International Journal of Multidisciplinary: Applied Business and Education Research, 2(5), 435-447. https://doi.org/10.11594/ijmaber.02.05.10
Pg Abu Bakar, D. N. N., Shahrill, M., & Zakariya, Y. F. (2023). Digital escape game and students’ learning outcomes in mathematics: Experience from Brunei. SAGE Open, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440231216838
Qian, M., & Clark, K. R. (2016). Game-based Learning and 21st century skills: A review of recent research. Computers in human Behavior, 63, 50-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.023
Rohaeti, E. E., Evans, B. R., Wiyatno, T., Prahmana, R. C. I., & Hidayat, W. (2023). Differential learning assisted with SANTUY mobile application for improving students’ mathematical understanding and ability. Journal on Mathematics Education, 14(2), 275-292. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v14i2.pp275-292
Sahni, J. (2019). Does blended learning enhance student engagement? Evidence from higher education. Journal of E-learning and Higher Education, 2019, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.5171/2019.121518
Salim, A. N., Jawawi, R., Shahrill, M., Jaidin, J. H., & Musa, J. (2023). Integrating game-based-learning to improve students’ essay writing in high school sociology. International Journal of Essential Competencies in Education, 2(1), 15-53. https://doi.org/10.36312/ijece.v2i1.1359
Shahabadi, M. M., & Uplane, M. (2015). Synchronous and asynchronous e-learning styles and academic performance of e-learners. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 176, 129-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.453
Simpol, N. S. H., Shahrill, M., Li, H. C., & Prahmana, R. C. I. (2017). Implementing thinking aloud pair and Pólya problem solving strategies in fractions. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 943(1), 012013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/943/1/012013
Siswono, T. Y. E., Rosyidi, A. H., Kohar, A. W., Hartono, S., Shahrill, M., & Uripno, G. (2024). What teachers know about integrating technology to enhance students’ mathematical creative thinking? AIP Conference Proceedings, 3046(1), 020049. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0195278
Skolastika, I. M. P. (2020). Boosting students’ participation through the implementation of virtual station rotation model. ELLITE: Journal of English Language, Literature, and Teaching, 5(2), 51-58.
Staker, H., & Horn, M. B. (2013). Blended Learning in the K—12 Education Sector. In A. G. Picciano, C. D. Dziuban, & C. R. Graham (Eds.), Blended Learning: Research Perspectives (Vol. 2). Routledge.
Suri, H. (2011). Purposeful sampling in qualitative research synthesis. Qualitative Research Journal, 11(2), 63-75. https://doi.org/10.3316/QRJ1102063
Szymkowiak, A., Melović, B., Dabić, M., Jeganathan, K., & Kundi, G. S. (2021). Information technology and Gen Z: The role of teachers, the internet, and technology in the education of young people. Technology in Society, 65, 101565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101565
Tavakol, M., & Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. International journal of medical education, 2, 53-55. https://doi.org/10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd
Timonen, P., & Ruokamo, H. (2021). Designing a preliminary model of coaching pedagogy for synchronous collaborative online learning. Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.1177/1834490921991430
Tomal, D. R. (2010). Action research for educators (2nd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Truitt, A. A., & Ku, H.-Y. (2018). A case study of third grade students’ perceptions of the station rotation blended learning model in the United States. Educational Media International, 55(2), 153-169. https://doi.org/10.1080/09523987.2018.1484042
VanVoorhis, C. R. W., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding Power and Rules of Thumb for Determining Sample Sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3(2), 43-50. https://doi.org/10.20982/tqmp.03.2.p043
Wahyuni, S., Sanjaya, I. G. M., Erman, E., & Jatmiko, B. (2019). Edmodo-based blended learning model as an alternative of science learning to motivate and improve junior high school students’ scientific critical thinking skills. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (Online), 14(7), 98-110. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v14i07.9980
Walne, M. B. (2012). Emerging blended-learning models and school profiles. Houston: Community Foundation. http://www.edustart.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/Emerging+BL+Models+and+School+Profiles+FINAL+09.21.12.pdf
Wang, L., Huang, Y., & Omar, M. K. (2021). Analysis of blended learning model application using text mining method. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 16(1), 172-187. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i01.19823
Willits, F. K., Theodori, G. L., & Luloff, A. E. (2016). Another look at Likert scales. Journal of Rural Social Sciences, 31(3), 126-139.
Wulandari, D., & Amir, M. F. (2022). Analysis of elementary school students' difficulties in fraction addition. Kreano, Jurnal Matematika Kreatif-Inovatif, 13(1), 43-54. https://doi.org/10.15294/kreano.v13i1.35275
Yang, H. H., Zhu, S., & MacLeod, J. (2016). Collaborative teaching approaches: Extending current blended learning models In S. K. S. Cheung, L.-f. Kwok, J. Shang, A. Wang, & R. Kwan, In Blended Learning: Aligning Theory with Practices, 9th International Conference, ICBL 2016, Cham (pp. 49-59). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41165-1_5
Zboun, J., & Farrah, M. (2021). Students’ perspectives of online language learning during corona pandemic: Benefits and challenges. Indonesian EFL Journal (IEFLJ), 7(1), 13-20.