The role of GeoGebra software in conceptual understanding and engagement among secondary school student
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
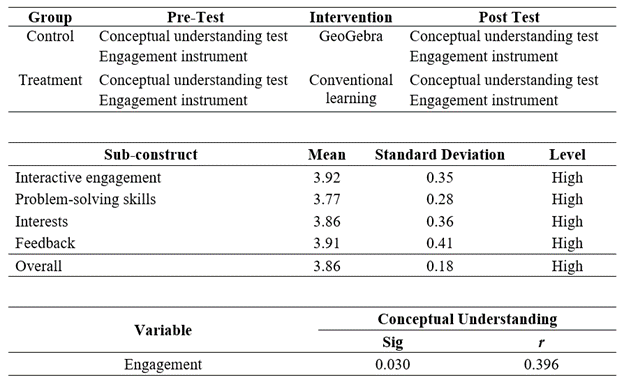
This study aims to identify the impact of GeoGebra software on conceptual understanding and engagement in the topic of Functions and Quadratic Equations in One Variable in high school. The study was conducted in a quasi-experimental design with 60 students at a secondary school in Muallim district. The study results were analyzed using descriptive statistics, inference, and the Pearson Correlation. Descriptive analysis indicates that students have a strong grasp of the topic taught, particularly showing high conceptual understanding and maximum engagement in interactive activities. Inference statistics reveal a significant difference in conceptual understanding levels between the treatment and control groups among Level Four students regarding Quadratic Functions and Equations in a Variable. In addition, there were significant differences in student engagement between the treatment and control groups. There is a significant relationship between the level of student engagement and students’ conceptual understanding of Quadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable for both groups. In conclusion, using GeoGebra software has an impact on the relationship between understanding the concept and involving students in learning the topic of Quadratic Functions and Equations in a Variable.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Abu-Baker, M. I. K., Abu-Zaid, M. K. S., Alsawalqah, H., Al-Shamayleh, Y., & Al-Shboul, B. (2019). The impact of the implementation of capability maturity model integration on user satisfaction: Case study on software companies in Jordan. Journal of Software, 14(7), 293-311. https://doi.org/10.17706/jsw.14.7.293-311
Al Mamun, M. A., & Lawrie, G. (2023). Student-content interactions: Exploring behavioural engagement with self-regulated inquiry-based online learning modules. Smart Learning Environments, 10(1), 1-31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-022-00221-x
Amelia, R., Kadarisma, G., Fitriani, N., & Ahmadi, Y. (2020). The effect of online mathematics learning on junior high school mathematic resilience during covid-19 pandemic. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1657(1), 012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1657/1/012011
Attard, C., & Holmes, K. (2022). An exploration of teacher and student perceptions of blended learning in four secondary mathematics classrooms. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 34(4), 719-740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-020-00359-2
Baring, C. C., & Alegre, E. M. (2019). Difficulties encountered in solving quadratic equation of the grade 9 students: Basis for constructing instructional materials. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 9(5), 271-277. https://doi.org/10.29322/ijsrp.9.05.2019.p8931
Bulatbaeva, K., Mukhamedkhanova, A., Toibazarova, N., Maigeldiyeva, S., Nurkasymova, S., & Rezuanova, G. (2023). Analysis of the relationships between school children’s technology addiction and school achievement. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 11(5), 1219-1237. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijemst.3622
Chang, H. S., Kim, J. Y., & Lee, B. (2022). Discourse analysis on understanding the differential concept of high school students in a dynamic geometry environment. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(7), em2127. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12152
Choo, Y. P., Renu, T., Raman, K., Wen, W. J., & Santhanasamy, V. D. S. (2019). Matematik tingkatan 4. Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia.
Christmas, D., Kudzai, C., & Josiah, M. (2013). Vygotsky’s zone of proximal development theory: What are its implications for mathematical teaching. Greener Journal of social sciences, 3(7), 371-377. https://doi.org/10.15580/gjss.2013.7.052213632
Creswell, J. W. (2021). A concise introduction to mixed methods research. SAGE publications.
Groening, C., & Binnewies, C. (2019). “Achievement unlocked!” - The impact of digital achievements as a gamification element on motivation and performance. Computers in human Behavior, 97, 151-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.02.026
Hamzah, N., Maat, S. M., & Ikhsan, Z. (2021). A systematic review on pupils’ misconceptions and errors in trigonometry. Pegem Journal of Education and Instruction, 11(4), 209-218. https://doi.org/10.47750/pegegog.11.04.20
Hamzah, N. A. H., & Hidayat, R. (2022). The role of Geogebra software in mathematics education: A systematic literature review. Jurnal Pendidikan Sains Dan Matematik Malaysia, 12(1), 24-38.
Hidayat, R., Kamarazan, N. A., Nasir, N., & Ayub, A. F. M. (2023). The effect of GeoGebra software on achievement and engagement among secondary school students. Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 17(4). https://doi.org/10.47836/mjms.17.4.06
Hidayat, R., & Wardat, Y. (2023). A systematic review of augmented reality in science, technology, engineering and mathematics education. Education and Information Technologies, 1-26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12157-x
Hiranyachattada, T., & Kusirirat, K. (2020). Using mobile augmented reality to enhancing students' conceptual understanding of physically-based rendering in 3D animation. European Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 8(1), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/9542
Leavy, P. (2022). Research design: Quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods, arts-based, and community-based participatory research approaches. Guilford Publications.
Malatjie, F., & Machaba, F. (2019). Exploring mathematics learners’ conceptual understanding of coordinates and transformation geometry through concept mapping. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 15(12), em1818. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/110784
Mardia, K. V. (1970). Measures of multivariate skewness and kurtosis with applications. Biometrika, 57(3), 519-530. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/57.3.519
Minarni, A., Napitupulu, E., & Husein, R. (2016). Mathematical understanding and representation ability of public junior high school in North Sumatra. Journal on Mathematics Education, 7(1), 43-56. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.7.1.2816.43-56
Mohd Saad, M. R., Mamat, S., Hidayat, R., & Othman, A. J. (2023). Integrating technology-based instruction and mathematical modelling for STEAM-based language learning: A sociocultural and self-determination theory perspective. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 17(14), 55-80. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v17i14.39477
Mutambara, L. H. N., Tendere, J., & Chagwiza, C. J. (2019). Exploring the conceptual understanding of the quadratic function concept in teachers’ colleges in Zimbabwe. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 16(2), em1817. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/112617
Nasir, M., Cari, C., Sunarno, W., & Rahmawati, F. (2022). The effect of STEM-based guided inquiry on light concept understanding and scientific explanation. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(11), em2175. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12499
Nzaramyimana, E., Mukandayambaje, E., Iyamuremye, L., Hakizumuremyi, V., & Ukobizaba, F. (2021). Effectiveness of GeoGebra towards students’ active learning, performance and interest to learn mathematics. International Journal of Mathematics and Computer Research, 9(10), 2423-2430. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijmcr/v9i10.05
Ozkan, G., & Topsakal, U. U. (2021). Investigating the effectiveness of STEAM education on students’ conceptual understanding of force and energy topics. Research in Science & Technological Education, 39(4), 441-460. https://doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2020.1769586
Pallant, J. (2020). SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using IBM SPSS. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003117452
Putra, Z. H., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., Dahnilsyah, D., & Hidayat, R. (2021). GeoGebra Integration in Elementary Initial Teacher Training: The Case of 3-D Shapes. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 15(19), 21-32. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v15i19.23773
Putri, N. W. S., & Wardika, I. W. G. (2020). Implementation TANDUR learning using GeoGebra towards student learning result viewed from independence learning. JTAM (Jurnal Teori Dan Aplikasi Matematika), 4(2), 115-121. https://doi.org/10.31764/jtam.v4i2.2384
Sahni, J. (2019). Does blended learning enhance student engagement? Evidence from higher education. Journal of E-learning and Higher Education, 2019, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.5171/2019.121518
Santiago, P. V. d. S., & Alves, F. R. V. (2022). Affine functions using GeoGebra: An investigation from the perspective of conceptual fields theory. Contemporary Mathematics and Science Education, 3(2), ep22013. https://doi.org/10.30935/conmaths/12112
Santos-Trigo, M. (2019). Mathematical problem solving and the use of digital technologies. In P. Liljedahl & M. Santos-Trigo (Eds.), Mathematical problem solving: Current themes, trends, and research (pp. 63-89). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10472-6_4
Selvanathan, M., Hussin, N. A. M., & Azazi, N. A. N. (2020). Students learning experiences during COVID-19: Work from home period in Malaysian Higher Learning Institutions. Teaching Public Administration, 41(1), 13-22. https://doi.org/10.1177/0144739420977900
Septian, A., Sugiarni, R., & Monariska, E. (2020). The application of android-based geogebra on quadratic equations material toward mathematical creative thinking ability. Al-Jabar: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 11(2), 261-272. https://doi.org/10.24042/ajpm.v11i2.6686
Shroff, R. H., Ting, F. S. T., & Lam, W. H. (2019). Development and validation of an instrument to measure students’ perceptions of technology-enabled active learning. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 35(4), 109-127. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.4472
Stephenson, C. R., Bonnes, S. L., Sawatsky, A. P., Richards, L. W., Schleck, C. D., Mandrekar, J. N., Beckman, T. J., & Wittich, C. M. (2020). The relationship between learner engagement and teaching effectiveness: a novel assessment of student engagement in continuing medical education. BMC Medical Education, 20(1), 403. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02331-x
Sukor, R., Ayub, A. F. M., Ab Rashid, N. K. M., & Halim, F. A. (2021). Relationship between students’ engagement with academic performance among non-food science students enrolled in food science course. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 18(4), 638-648. https://doi.org/10.36681/tused.2021.95
Utami, N. S., & Jupri, A. (2021). Students’ structure sense ability in solving quadratic equation problems. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1806(1), 012061. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1806/1/012061
Wilcox, R. R. (2009). Comparing pearson correlations: Dealing with heteroscedasticity and nonnormality. Communications in Statistics - Simulation and Computation, 38(10), 2220-2234. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610910903289151
Yatim, S. S. K. M., Saleh, S., Zulnaidi, H., Yew, W. T., & Yatim, S. A. M. (2022). Effects of brain-based teaching approach integrated with GeoGebra (B-Geo Module) on students' conceptual understanding. International Journal of Instruction, 15(1), 327-346. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2022.15119a
Yohannes, A., & Chen, H.-L. (2023). GeoGebra in mathematics education: a systematic review of journal articles published from 2010 to 2020. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(9), 5682-5697. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.2016861
Yoon, H., Bae, Y., Lim, W., & Kwon, O. N. (2021). A story of the national calculus curriculum: how culture, research, and policy compete and compromise in shaping the calculus curriculum in South Korea. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(3), 663-677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01219-w
Zainuddin, Z., Shujahat, M., Haruna, H., & Chu, S. K. W. (2020). The role of gamified e-quizzes on student learning and engagement: An interactive gamification solution for a formative assessment system. Computers & Education, 145, 103729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103729
Zulnaidi, H., Oktavika, E., & Hidayat, R. (2020). Effect of use of GeoGebra on achievement of high school mathematics students. Education and Information Technologies, 25(1), 51-72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09899-y