Development of mobile augmented reality-based geometry learning games to facilitate spatial reasoning
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
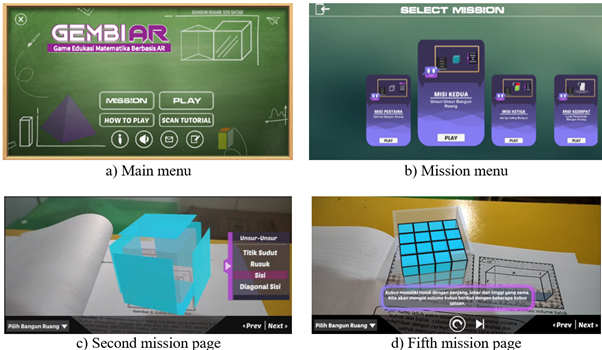
Geometry learning requires a comprehensive understanding of spatial reasoning, but students face difficulty in mastering the skill. As a virtual technology, Augmented Reality (AR) offers a solution to overcome the challenges in spatial reasoning with the potential to represent and manipulate objects and develop spatial images mentally. Therefore, this research aimed to develop a mobile educational game named GEMBI AR to support students' spatial reasoning skills in geometry learning. The ADDIE model consists of analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation phases used to conduct research and development (R&D). The participants included six expert validators, two mathematics teachers, and eighteen eighth graders. In addition, the expert validators validated GEMBI AR in terms of quality. The result showed that GEMBI AR was valid as a geometry learning tool. According to the feedback of teachers and students, GEMBI AR was practical for educational purposes since the application positively impacted spatial reasoning. Students' spatial reasoning skills were also enhanced to compare the differences in the pre-test and post-test using Wilcoxon (Z = –3.578, p = 0.000 < 0.05). Meanwhile, the N-Gain score of 0.576, showing moderate improvement, reflected gains in spatial perception, mental rotation, and visualization. These findings suggest that GEMBI AR is a functional and valid educational resource useful for helping students develop geometric spatial reasoning. Thus, geometry learning supported by GEMBI AR has the potential to enhance spatial reasoning in secondary school.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Agrawal, S., Simon, A., Bech, S., Bærentsen, K., & Forchhammer, S. (2020). Defining immersion: Literature review and implications for research on immersive audiovisual experiences. Journal of Audio Engineering Society, 68(6), 404-417. https://doi.org/10.17743/jaes.2020.0039
Ahmad, N. I. N., & Junaini, S. N. (2020). Augmented reality for learning mathematics: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(16), 106-122. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v15i16.14961
Aiken, L. R. (1985). Three coefficients for analyzing the reliability and validity of ratings. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 45(1), 131-142. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164485451012
Al-Amri, S., Hamid, S., Noor, N. F. M., & Gani, A. (2023). A framework for designing interactive mobile training course content using augmented reality. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82(20), 30491-30541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14561-4
Alkhattabi, M. (2017). Augmented reality as e-learning tool in primary schools' education: Barriers to teachers' adoption. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 12(2), 91-100. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v12i02.6158
Anggraini, S., Setyaningrum, W., Retnawati, H., & Marsigit, M. (2020). How to improve critical thinking skills and spatial reasoning with augmented reality in mathematics learning? Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1581(1), 012066. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1581/1/012066
Anwar, L., Goedhart, M. J., & Mali, A. (2023). Learning trajectory of geometry proof construction: Studying the emerging understanding of the structure of Euclidean proof. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 19(5), em2266. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13160
Atit, K., Power, J. R., Pigott, T., Lee, J., Geer, E. A., Uttal, D. H., Ganley, C. M., & Sorby, S. A. (2022). Examining the relations between spatial skills and mathematical performance: A meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 29(3), 699-720. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-021-02012-w
Atit, K., Power, J. R., Veurink, N., Uttal, D. H., Sorby, S., Panther, G., Msall, C., Fiorella, L., & Carr, M. (2020). Examining the role of spatial skills and mathematics motivation on middle school mathematics achievement. International journal of STEM education, 7(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00234-3
Baxter, G., & Hainey, T. (2024). Using immersive technologies to enhance the student learning experience. Interactive Technology and Smart Education, 21(3), 403-425. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-05-2023-0078
Bizami, N. A., Tasir, Z., & Kew, S. N. (2023). Innovative pedagogical principles and technological tools capabilities for immersive blended learning: a systematic literature review. Education and Information Technologies, 28(2), 1373-1425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11243-w
Branch, R. M. (2009). Instructional design: The ADDIE approach. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09506-6
Buckley, J., Seery, N., & Canty, D. (2019). Investigating the use of spatial reasoning strategies in geometric problem solving. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 29(2), 341-362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-018-9446-3
Cao, Y., Ng, G.-W., & Ye, S.-S. (2023). Design and evaluation for immersive virtual reality learning environment: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 15(3), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031964
Carrera, C. C., & Asensio, L. A. B. (2017). Augmented reality as a digital teaching environment to develop spatial thinking. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 44(3), 259-270. https://doi.org/10.1080/15230406.2016.1145556
Cheng, Y.-L., & Mix, K. S. (2014). Spatial training improves children's mathematics ability. Journal of Cognition and Development, 15(1), 2-11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15248372.2012.725186
Cohen, C. A., & Hegarty, M. (2014). Visualizing cross sections: Training spatial thinking using interactive animations and virtual objects. Learning and Individual Differences, 33, 63-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2014.04.002
Costa, M. C., Manso, A., & Patrício, J. (2020). Design of a mobile augmented reality platform with game-based learning purposes. Information, 11(3), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11030127
Dengel, A. (2022). What Is Immersive Learning? In 2022 8th International Conference of the Immersive Learning Research Network (iLRN), (pp. 1-5). https://doi.org/10.23919/iLRN55037.2022.9815941
Di, X., & Zheng, X. (2022). A meta-analysis of the impact of virtual technologies on students’ spatial ability. Educational Technology Research and Development, 70(1), 73-98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-022-10082-3
Do, T. V., & Lee, J.-W. (2009). A multiple-level 3D-LEGO game in augmented reality for improving spatial ability. In Human-Computer Interaction. Interacting in Various Application Domains, Berlin, Heidelberg (pp. 296-303). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02583-9_33
Evidiasari, S., Subanji, S., & Irawati, S. (2019). Students’ spatial reasoning in solving geometrical transformation problems. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE), 1(2), 38-51. https://doi.org/10.23917/ijolae.v1i2.8703
Gargrish, S., Mantri, A., & Kaur, D. P. (2020). Augmented reality-based learning environment to enhance teaching-learning experience in geometry education. Procedia Computer Science, 172, 1039-1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.05.152
Gargrish, S., Mantri, A., & Kaur, D. P. (2022). Evaluation of memory retention among students using augmented reality based geometry learning assistant. Education and Information Technologies, 27(9), 12891-12912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11147-9
Hanggara, Y., Qohar, A., & Sukoriyanto, S. (2024). The impact of augmented reality-based mathematics learning games on students' critical thinking skills. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 18(7), 173–187. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v18i07.48067
Harris, D., Logan, T., & Lowrie, T. (2023). Spatial visualization and measurement of area: A case study in spatialized mathematics instruction. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 70, 101038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2023.101038
Hawes, Z. C. K., Gilligan-Lee, K. A., & Mix, K. S. (2022). Effects of spatial training on mathematics performance: A meta-analysis. Developmental Psychology, 58(1), 112-137. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001281
Hisyam, F. N., Sukoriyanto, S., & Sulandra, I. M. (2023). Penalaran spasial siswa SMP pada materi geometri bangun ruang berdasarkan tipe kepribadian ekstrovert dan introvert [Junior high school students' spatial reasoning on geometric material based on extrovert and introvert personality types]. Jurnal Cendekia: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 7(3), 2990-3005. https://doi.org/10.31004/cendekia.v7i3.2500
İbili, E., Çat, M., Resnyansky, D., Şahin, S., & Billinghurst, M. (2020). An assessment of geometry teaching supported with augmented reality teaching materials to enhance students’ 3D geometry thinking skills. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 51(2), 224-246. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2019.1583382
Ikhsan, M., Rochaminah, S., & Mastura, A. (2024). The development of Geo-Math application by integrating Geo-Gebra applets to improve students’ spatial ability. Jurnal Ilmiah Peuradeun, 12(3), 1129-1154. https://doi.org/10.26811/peuradeun.v12i3.1492
Ismail, H., Abdullah, A. H., Alhassora, N. S. A., & Noh, N. H. (2020). Investigating student’s learning difficulties in Shape and Space topic: A case study. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(5), 5315-5321.
Krüger, J. M., Palzer, K., & Bodemer, D. (2022). Learning with augmented reality: Impact of dimensionality and spatial abilities. Computers and Education Open, 3, 100065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeo.2021.100065
Lai, J. W., & Cheong, K. H. (2022). Adoption of Virtual and Augmented Reality for Mathematics Education: A Scoping Review. IEEE Access, 10, 13693-13703. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3145991
Lee, K. (2012). Augmented reality in education and training. TechTrends, 56(2), 13-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-012-0559-3
Lombardi, C. M., Casey, B. M., Pezaris, E., Shadmehr, M., & Jong, M. (2019). Longitudinal analysis of associations between 3-D mental rotation and mathematics reasoning skills during middle school: Across and within genders. Journal of Cognition and Development, 20(4), 487-509. https://doi.org/10.1080/15248372.2019.1614592
Lowrie, T., Harris, D., Logan, T., & Hegarty, M. (2021). The impact of a spatial intervention program on students’ spatial reasoning and mathematics performance. The journal of experimental education, 89(2), 259-277. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2019.1684869
MacDowell, P., & Lock, J. (2022). Immersive education: Designing for learning. Springer Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18138-2
Maeda, Y., & Yoon, S. Y. (2013). A meta-analysis on gender differences in mental rotation ability measured by the purdue spatial visualization tests: visualization of rotations (PSVT:R). Educational Psychology Review, 25(1), 69-94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-012-9215-x
Magomadov, V. S. (2020). Examining the potential of VR and AR technologies for education. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1691(1), 012160. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1691/1/012160
Mandala, A. S., & Setyaningrum, W. (2024). Development of mobile augmented reality application for geometry in mathematics learning. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2622(1), 090007. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0133554
Meltzer, D. E. (2002). The relationship between mathematics preparation and conceptual learning gains in physics: A possible “hidden variable” in diagnostic pretest scores. American Journal of Physics, 70(12), 1259-1268. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.1514215
Mohsen, M. A., & Alangari, T. S. (2024). Analyzing two decades of immersive technology research in education: Trends, clusters, and future directions. Education and Information Technologies, 29(3), 3571-3587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11968-2
Mulligan, J. (2015). Looking within and beyond the geometry curriculum: connecting spatial reasoning to mathematics learning. Zdm, 47(3), 511-517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-015-0696-1
Murtafiah, W., Sa’dijah, C., Chandra, T. D., & Susiswo, S. (2019). Decision making of the winner of the national student creativity program in designing ICT-based learning media. TEM Journal, 8(3), 1039-1045. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM83-49
Mystakidis, S., & Lympouridis, V. (2023). Immersive Learning. Encyclopedia, 3(2), 396-405. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3020026
Nadzeri, M. B., Musa, M., Chew, C. M., & Ismail, I. M. (2023). Teachers’ perspectives on the development of augmented reality application in geometry topic for elementary school. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 17(15), 38-52. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v17i15.40097
Nindiasari, H., Pranata, M. F., Sukirwan, S., Sugiman, S., Fathurrohman, M., Ruhimat, A., & Yuhana, Y. (2024). The use of augmented reality to improve students' geometry concept problem-solving skills through the STEAM approach. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 119-138. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p119-138
Otálora, Y., & Taborda-Osorio, H. (2025). Contributions of numeral knowledge, spatial reasoning, and numerical mapping to first graders’ arithmetic and geometric skills. Cognitive Development, 73, 101520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2024.101520
Papakostas, C., Troussas, C., Krouska, A., & Sgouropoulou, C. (2021). Exploration of augmented reality in spatial abilities training: A systematic literature review for the last decade. Informatics in Education, 20(1), 107-130. https://doi.org/10.15388/infedu.2021.06
Papakostas, C., Troussas, C., Krouska, A., & Sgouropoulou, C. (2023). Exploring users’ behavioral intention to adopt mobile augmented reality in education through an extended technology acceptance model. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 39(6), 1294-1302. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2062551
Prasetya, F., Fortuna, A., Samala, A. D., Rawas, S., Mystakidis, S., Syahril, S., Waskito, W., Primawati, P., Wulansari, R. E., & Kassymova, G. K. (2024). The impact of augmented reality learning experiences based on the motivational design model: A meta-analysis. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 10, 100926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2024.100926
Putri, A., Wahyuningsih, T., Ananti, N. S., Wicaksono, A., Shofa, G. Z., As’ari, A. R., Purwanto, P., & Osman, S. (2023). EUCLIDA: 3D augmented reality card for learning numeracy about geometry. TEM Journal, 12(2), 1174-1181. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM122-63
Ramful, A., Lowrie, T., & Logan, T. (2017). Measurement of spatial ability: Construction and validation of the spatial reasoning instrument for middle school students. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 35(7), 709-727. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282916659207
Retnawati, H. (2016). Analisis kuantitatif instrumen penelitian (panduan peneliti, mahasiswa, dan psikometrian) [Quantitative analysis of research instruments (guide for researchers, students and psychometricians)]. Parama publishing.
Rich, K., & Brendefur, J. L. (2018). The importance of spatial reasoning in early childhood mathematics. In D. Farland-Smith (Ed.), Early Childhood Education. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.81564
Richardo, R., Wijaya, A., Rochmadi, T., Abdullah, A. A., Nurkhamid, N., Astuti, A. W., & Hidayah, K. N. (2023). Ethnomathematics augmented reality: Android-based learning multimedia to improve creative thinking skills on geometry. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 13(4), 731-737. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2023.13.4.1860
Sa'dijah, C., Murtafiah, W., Anwar, L., Nurhakiki, R., & Cahyowati, E. T. D. (2021). Teaching higher order thinking skills in mathematics classrooms: Gender differences. Journal on Mathematics Education, 12(1), 159-180. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.12.1.13087.159-180
Septia, T., Prahmana, R. C. I., Pebrianto, P., & Wahyu, R. (2018). Improving students spatial reasoning with course lab. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(2), 327-336. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.3462.327-336
Shaukat, S. M. (2023). Exploring the potential of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in education. International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology (IJARSCT), 3(2), 51-56. https://doi.org/10.48175/IJARSCT-12108
Singh, G., Singh, G., Tuli, N., & Mantri, A. (2024). Hyperspace AR: an augmented reality application to enhance spatial skills and conceptual knowledge of students in trigonometry. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83(21), 60881-60902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17870-w
Songkram, N., Songkram, N., Chootongchai, S., & Samanakupt, T. (2021). Developing students’ learning and innovation skills using the virtual smart classroom. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 16(4), 34-51. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i04.15221
Su, Y.-S., Cheng, H.-W., & Lai, C.-F. (2022). Study of virtual reality immersive technology enhanced mathematics geometry learning. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 760418. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.760418
Supli, A. A., & Yan, X. (2024). Exploring the effectiveness of augmented reality in enhancing spatial reasoning skills: A study on mental rotation, spatial orientation, and spatial visualization in primary school students. Education and Information Technologies, 29(1), 351-374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12255-w
Sutarni, S., Sutama, S., Prayitno, H. J., Sutopo, A., & Laksmiwati, P. A. (2024). The development of realistic mathematics education-based student worksheets to enhance higher-order thinking skills and mathematical ability. Infinity Journal, 13(2), 285-300. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i2.p285-300
Wang, Y. (2022). Effects of augmented reality game-based learning on students’ engagement. International Journal of Science Education, Part B, 12(3), 254-270. https://doi.org/10.1080/21548455.2022.2072015
Wijayanto, Z., Setiana, D. S., & Kusumaningrum, B. (2022). The development of online learning game on linear program courses. Infinity Journal, 11(1), 133-144. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i1.p133-144
Woolcott, G., Le Tran, T., Mulligan, J., Davis, B., & Mitchelmore, M. (2022). Towards a framework for spatial reasoning and primary mathematics learning: an analytical synthesis of intervention studies. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 34(1), 37-67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-020-00318-x
Wu, J., Jiang, H., Long, L., & Zhang, X. (2024). Effects of AR mathematical picture books on primary school students' geometric thinking, cognitive load and flow experience. Education and Information Technologies, 29(18), 24627-24652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12768-y
Wulandari, S., Sa’dijah, C., Irawan, E. B., & Sulandra, I. M. (2019). Spatial information processing of seventh grader in solving Geometry problems. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 243(1), 012135. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/243/1/012135