Computational thinking ability in mathematics learning of exponents in grade IX
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
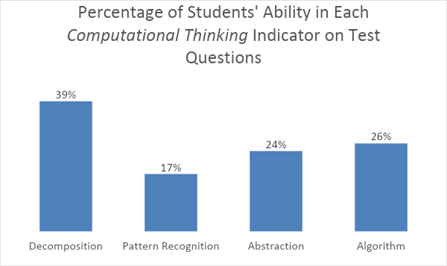
In the PISA 2021 framework, Computational Thinking (CT) is described as a detailed mathematical solution to the problem to be solved. However, CT-based learning still needs to be widely applied in Indonesia. This study aims to describe the CT ability of students in grade IX of junior high school based on CT indicators on the material of signed numbers. The data collection techniques in this study were test questions and interviews. Students who obtained high categories with scores above 45.76 were six students with a percentage of 21%, students who received medium categories with scores between 11.94 and 45.76 were 19 students with a rate of 66%, and students who obtained low categories with scores below 11.94 were four people with a percentage of 13%. The results of the study state that as many as 39% of students can decompose the problems given, 17% of students can recognize patterns in the problem, 24% of students can sort out the information in the situation or abstract, and 26% of students can solve problems well according to algorithm indicators.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Aisy, A. R., & Hakim, D. L. (2023). Kemampuan berfikir komputasi matematis siswa SMP pada materi pola bilangan [Mathematical computational thinking abilities of junior high school students in number pattern material]. Didactical Mathematics, 5(2), 348-360.
Amalia, A. R., Rusdi, R., & Kamid, K. (2021). Pengembangan soal matematika bermuatan HOTS setara PISA berkonteks pancasila [Development of mathematics questions containing HOTS equivalent to PISA in the Pancasila context]. Jurnal Cendekia: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 5(1), 1-19. https://doi.org/10.31004/cendekia.v5i1.386
Angraini, L. M., Arcat, A., & Sohibun, S. (2022). Pengaruh bahan ajar berbasis multimedia interaktif terhadap kemampuan computational thinking matematis mahasiswa [The influence of interactive multimedia-based teaching materials on students' mathematical computational thinking abilities]. JNPM (Jurnal Nasional Pendidikan Matematika), 6(2), 370-383. https://doi.org/10.33603/jnpm.v6i2.6937
Ariesandi, I., Syamsuri, S., Yuhana, Y., & Fatah, A. (2021). Analisis kebutuhan pengembangan modul elektronik berbasis inkuiri untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berpikir komputasi pada materi barisan dan deret siswa SMA [Analysis of the need for developing inquiry-based electronic modules to improve computational thinking skills in high school students' sequence and series material]. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Matematika dan Pendidikan Matematika, 12(2), 178-190.
Bilbao, J., Bravo, E., García, O., Rebollar, C., & Varela, C. (2021). Study to find out the perception that first year students in engineering have about the computational thinking skills, and to identify possible factors related to the ability of abstraction. Heliyon, 7(2), e06135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06135
Bråting, K., & Kilhamn, C. (2021). Exploring the intersection of algebraic and computational thinking. Mathematical thinking and learning, 23(2), 170-185. https://doi.org/10.1080/10986065.2020.1779012
Chahyadi, F., Bettiza, M., Ritha, N., Rathomi, M. R., & Hayaty, N. (2021). Peningkatan high order thinking skill siswa melalui pendampingan computational thinking [Improvement of students' high-order thinking skills through computational thinking assistance]. Jurnal Anugerah, 3(1), 25-36.
Chytas, C., van Borkulo, S. P., Drijvers, P., Barendsen, E., & Tolboom, J. L. J. (2024). Computational thinking in secondary mathematics education with GeoGebra: Insights from an intervention in calculus lessons. Digital Experiences in Mathematics Education, 1-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40751-024-00141-0
Dimyati, A., Fatra, M., Sobirudin, D., & Hafiz, M. (2023). Pengembangan media motion graphic pada mata kuliah aplikasi matematika komputer [Development of motion graphic media in computer mathematics applications courses]. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 12(1), 67-79. https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v12i1.6444
Fajri, M., & Utomo, E. (2019). Computational thinking, mathematical thinking berorientasi gaya kognitif pada pembelajaran matematika di sekolah dasar [Computational thinking, mathematical thinking is cognitive style oriented in mathematics learning in elementary schools]. Dinamika Sekolah Dasar, 1(1), 1-18.
Grover, S., & Pea, R. (2018). Computational thinking: A competency whose time has come. Computer science education: Perspectives on teaching and learning in school, 19(1), 19-38. https://doi.org/10.5040/9781350057142.ch-003
Jamna, N. D., Hamid, H., & Bakar, M. T. (2022). Analisis kemampuan berpikir komputasi matematis siswa smp pada materi persamaan kuadrat [Analysis of junior high school students' mathematical computational thinking abilities on quadratic equations]. Jurnal Pendidikan Guru Matematika, 2(3), 278-288. https://doi.org/10.33387/jpgm.v2i3.5149
Kadarwati, S., Suparman, S., & Astutik, K. (2020). Keefektifan Computational Thingking (CT) Dan Problem Based Learning (PBL) Dalam Meningkatkan Kreativitas Siswa Terhadap Penyelesaian Soal-Soal Cerita Materi Perbandingan (Skala Pada Peta) Di Sekolah Dasar [The effectiveness of computational thinking (CT) and problem-based learning (PBL) in increasing students' creativity in solving comparative material story problems (scales on maps) in elementary schools]. Jurnal Karya Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 63-68. https://doi.org/10.26714/jkpm.7.1.2020.63-68
Kamil, M. R. (2021). Analisis kemampuan berpikir komputasional matematis Siswa Kelas IX SMP Negeri 1 Cikampek pada materi pola bilangan [Analysis of mathematical computational thinking abilities of Class IX Students of SMP Negeri 1 Cikampek on number pattern material]. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Matematika dan Pendidikan Matematika, 12(2), 259-270.
Kresnadi, H., Ghasya, D. A. V., & Pranata, R. (2023). Analisis kemampuan computational thinking berdasarkan tahap generalisasi pola dan desain algoritma siswa di kelas III SDN 03 Toho [Analysis of computational thinking abilities based on the pattern generalization and algorithm design stages of students in class III at SDN 03 Toho]. Jurnal Review Pendidikan dan Pengajaran (JRPP), 6(4), 1660-1666.
Kynigos, C., & Grizioti, M. (2018). Programming approaches to computational thinking: Integrating turtle geometry, dynamic manipulation and 3D space. Informatics in Education, 17(2), 321-340. https://doi.org/10.15388/infedu.2018.17
Lagalante, R., Suharna, H., & Tonra, W. S. (2022). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan masalah matematika pada bilangan berpangkat dan bentuk akar [Analysis of student errors in solving mathematical problems on exponent numbers and root forms]. Jurnal Pendidikan Guru Matematika, 2(2), 184-192. https://doi.org/10.33387/jpgm.v2i2.4633
Lamprou, A., & Repenning, A. (2018). Teaching how to teach computational thinking In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, Larnaca, Cyprus (pp. 69–74). https://doi.org/10.1145/3197091.3197120
Lee, S. W.-Y., Tu, H.-Y., Chen, G.-L., & Lin, H.-M. (2023). Exploring the multifaceted roles of mathematics learning in predicting students' computational thinking competency. International journal of STEM education, 10(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-023-00455-2
Lestari, A. C., & Annizar, A. M. r. (2020). Proses berpikir kritis siswa dalam menyelesaikan masalah PISA ditinjau dari kemampuan berpikir komputasi [Students' critical thinking processes in solving PISA problems are viewed from computational thinking skills]. Jurnal Kiprah, 8(1), 46-55.
Lewis Presser, A. E., Young, J. M., Rosenfeld, D., Clements, L. J., Kook, J. F., Sherwood, H., & Cerrone, M. (2023). Data collection and analysis for preschoolers: An engaging context for integrating mathematics and computational thinking with digital tools. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 65, 42-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2023.05.012
Litia, N., Sinaga, B., & Mulyono, M. (2023). Profil berpikir komputasi siswa dengan menggunakan model pembelajaran problem based learning (PBL) ditinjau dari gaya belajar di SMA N 1 Langsa [Computational thinking profile of students using the problem based learning (PBL) learning model in terms of learning styles at SMA N 1 Langsa]. Jurnal Cendekia: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 7(2), 1508-1518. https://doi.org/10.31004/cendekia.v7i2.2270
Maharani, S., Kholid, M. N., Pradana, L. N., & Nusantara, T. (2019). Problem solving in the context of computational thinking. Infinity Journal, 8(2), 109-116. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v8i2.p109-116
Manullang, S. B., & Simanjuntak, E. (2023). Pengaruh model problem based learning terhadap kemampuan computational thinking berbantuan media Geogebra [The influence of the problem based learning model on computational thinking abilities assisted by Geogebra media]. Journal on Education, 6(1), 7786-7796.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
Montuori, C., Gambarota, F., Altoé, G., & Arfé, B. (2024). The cognitive effects of computational thinking: A systematic review and meta-analytic study. Computers & Education, 210, 104961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104961
Mulyono, B., & Hapizah, H. (2018). Pemahaman konsep dalam pembelajaran matematika [Understanding concepts in mathematics learning]. Kalamatika: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 3(2), 103-122. https://doi.org/10.22236/KALAMATIKA.vol3no2.2018pp103-122
Munirah, S. (2022). Pengembangan bahan ajar matematika siswa SMA berorientasi computational thinking skills. Doctoral dissertation. Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. Retrieved from https://repository.upi.edu/71642
Noviyanti, N., Yuniarti, Y., & Lestari, T. (2023). Pengaruh pembelajaran berdiferensiasi terhadap kemampuan computational thinking siswa sekolah dasar [The effect of differentiated learning on elementary school students' computational thinking abilities]. Prima Magistra: Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan, 4(3), 283-293. https://doi.org/10.37478/jpm.v4i3.2806
Nurkamilah, P., & Afriansyah, E. A. (2021). Analisis miskonsepsi siswa pada bilangan berpangkat [Analysis of students' misconceptions about exponent numbers]. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 10(1), 49-60.
Piatti, A., Adorni, G., El-Hamamsy, L., Negrini, L., Assaf, D., Gambardella, L., & Mondada, F. (2022). The CT-cube: A framework for the design and the assessment of computational thinking activities. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 5, 100166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100166
Setyawan, F., & Astuti, D. (2021). Pengembangan bahan ajar kalkulus integral berbasis pendekatan computational thinking [Development of integral calculus teaching materials based on a computational thinking approach]. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 10(4), 2000-2013. https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v10i4.4308
Sumirat, S. F. P., Sudihartinih, E., & Sumiaty, E. (2023). Kajian learning obstacle pada topik bilangan berpangkat ditinjau dari literasi PISA 2021 [Study of learning obstacles on the topic of exponent numbers in terms of PISA 2021 literacy]. Jurnal Cendekia: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 350-361.
Sunardiningsih, G. W., Hariyani, S., & Fayeldi, T. (2019). Analisis kesalahan siswa dalam menyelesaikan soal matematika berdasarkan analisis Newman [Analysis of student errors in solving mathematics problems based on Newman's analysis]. RAINSTEK: Jurnal Terapan Sains & Teknologi, 1(2), 41-45.
Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
Wing, J. M. (2006). Computational thinking. Communications of the ACM, 49(3), 33–35. https://doi.org/10.1145/1118178.1118215
Wu, T.-T., Silitonga, L. M., & Murti, A. T. (2024). Enhancing English writing and higher-order thinking skills through computational thinking. Computers & Education, 213, 105012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105012
Zahid, M. Z. (2020). Telaah kerangka kerja PISA 2021: Era integrasi computational thinking dalam bidang matematika [Review the PISA 2021 framework: The era of the integration of computational thinking in the field of mathematics]. In PRISMA, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Matematika, Universitas Negeri Semarang (Vol. 3, pp. 706-713).