Global trends in flipped classroom research within mathematics education over past two decade: A bibliometric analysis
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
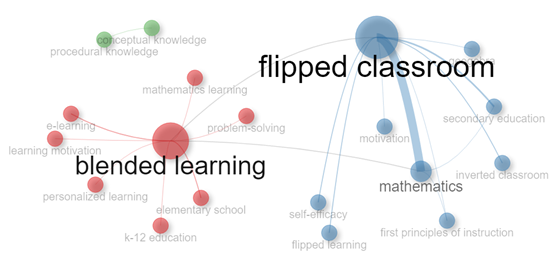
This research aims to provide a bibliometric review of trends in using flipped classrooms in mathematics learning research. This research is essential to analyze the extent of the flipped classroom research trend in mathematics learning as a reference for future research in this research. Bibliometric analysis was used to analyze and classify bibliographic data by considering inclusion and exclusion criteria. The database used was Scopus using the Bibliometrix application. The search was carried out using the keywords "flipped classroom", "mathematics learning", and "K-12". The results revealed a total of 102 articles related to the keywords. The data showed increased publications over the last two decades, with 2023 being the year with the highest publication count. Apart from that, Indonesia had the highest rate of producing related articles. The most relevant author was Hew Khe Foon. The most cited article was "A self-regulated flipped classroom approach to improving students' learning performance in a mathematics course". The Indonesian Education University was the most productive affiliate related to this theme. Furthermore, the journal "Educational Technology and Society" was found to be the most prolific journal for publishing research outcomes. New themes emerged in flipped classroom research, such as conceptual and procedural knowledge. Future researchers are expected to utilize the research focus to determine the theme to be explored. It is recommended that further researchers incorporate the novelty discussed in this research.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959-975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Azizah, T., Fauzan, A., & Harisman, Y. (2022). "Flipped classroom type peer instruction-based learning" based on a website to improve student's problem solving. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 325-348. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p325-348
Bergmann, J., & Sams, A. (2012). Flip your classroom: Reach every student in every class every day. International society for technology in education.
Bhagat, K. K., Chang, C.-N., & Chang, C.-Y. (2016). The impact of the flipped classroom on mathematics concept learning in high school. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 19(3), 134-142.
Bond, M., Buntins, K., Bedenlier, S., Zawacki-Richter, O., & Kerres, M. (2020). Mapping research in student engagement and educational technology in higher education: a systematic evidence map. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 17(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0176-8
Brahimi, T., & Sarirete, A. (2015). Learning outside the classroom through MOOCs. Computers in human Behavior, 51, 604-609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.03.013
Butzler, K. B. (2015). ConfChem conference on flipped classroom: Flipping at an open-enrollment college. Journal of Chemical Education, 92(9), 1574-1576. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed500875n
Butzler, K. B. (2016). The synergistic effects of self-regulation tools and the flipped classroom. Computers in the Schools, 33(1), 11-23. https://doi.org/10.1080/07380569.2016.1137179
del Arco, I., Mercadé-Melé, P., Ramos-Pla, A., & Flores-Alarcia, Ò. (2022). Bibliometric analysis of the flipped classroom pedagogical model: Trends and strategic lines of study. Frontiers in Education, 7, 1022295. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.1022295
Demir, M., Zengin, Y., Özcan, Ş., Urhan, S., & Aksu, N. (2023). Students’ mathematical reasoning on the area of the circle: 5E-based flipped classroom approach. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 54(1), 99-123. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2022.2101955
Egara, F. O., & Mosimege, M. (2023). Effect of flipped classroom learning approach on mathematics achievement and interest among secondary school students. Education and Information Technologies, 29(7), 8131-8150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12145-1
Egara, F. O., & Mosimege, M. (2024). Effect of blended learning approach on secondary school learners’ mathematics achievement and retention. Education and Information Technologies, 1-26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12651-w
Faryanti, F., & Efendi, R. (2023). Analisis bibliometrik model flipped classroom learning untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berpikir kritis [Bibliometric analysis of the flipped classroom learning model to improve critical thinking skills]. Innovative: Journal Of Social Science Research, 3(5), 5350-5370.
Fatimah, O. L., Adiningsih, R., Lubis, F. D., & Fathani, A. H. (2022). The effect of flipped classroom learning in enhancing mathematics learning outcomes of blind students during the pandemic. Numerical: Jurnal Matematika dan Pendidikan Matematika, 6(1), 37-48. https://doi.org/10.25217/numerical.v6i1.2320
Fauzi, A. (2019). Redefining learning process through flipped classroom. Konstruktivisme: Jurnal Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran, 11(2), 114-122. https://doi.org/10.35457/konstruk.v11i2.719
Fernández-Martín, F.-D., Romero-Rodríguez, J.-M., Gómez-García, G., & Ramos Navas-Parejo, M. (2020). Impact of the flipped classroom method in the mathematical area: A systematic review. Mathematics, 8(12), 2162. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8122162
Firdaus, F. M., Pratiwi, N. A., Riyani, S., & Utomo, J. (2021). Meningkatkan kemandirian belajar peserta didik sekolah dasar menggunakan model SOLE saat pandemi COVID-19 [Increasing the self-regulated learning of elementary school students using the SOLE model during the COVID-19 pandemic]. Foundasia, 12(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.21831/foundasia.v12i1.37786
Flipped Learning Network (FLN). (2014). The Four Pillars of F-L-I-P™. Retrieved from https://flippedlearning.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/FLIP_handout_FNL_Web.pdf
Fung, C.-H. (2020). How does flipping classroom foster the STEM education: A case study of the FPD model. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 25(3), 479-507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-020-09443-9
Fung, C.-H., Poon, K.-K., Besser, M., & Fung, M.-C. (2024). Improving short-term academic performance in the flipped classroom using dynamic geometry software. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 40(2), 775-786. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12914
Garrison, D. R., & Vaughan, N. D. (2008). Blended learning in higher education: Framework, principles, and guidelines. John Wiley & Sons.
Gok, D., & Bozoglan, H. (2016). Prospective English language teachers’ perceptions towards a new paradigm in foreign language education: Flipped classroom model. Journal of Foreign Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.14706/jfltal16326
Gough, E., DeJong, D., Grundmeyer, T., & Baron, M. (2017). K-12 teacher perceptions regarding the flipped classroom model for teaching and learning. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 45(3), 390-423. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047239516658444
Grover, S., Pea, R., & Cooper, S. (2015). Designing for deeper learning in a blended computer science course for middle school students. Computer Science Education, 25(2), 199-237. https://doi.org/10.1080/08993408.2015.1033142
Herutomo, R. A., & Masrianingsih, M. (2021). Pembelajaran flipped classroom berpendekatan matematika realistik untuk mendukung literasi matematis siswa [Flipped classroom learning with a realistic mathematics approach to support students' mathematical literacy]. Jurnal Karya Pendidikan Matematika, 8(2), 45-52. https://doi.org/10.26714/jkpm.8.2.2021.45-52
Hidayat, W., & Aripin, U. (2023). How to develop an e-LKPD with a scientific approach to achieving students' mathematical communication abilities? Infinity Journal, 12(1), 85-100. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i1.p85-100
Hudson, C. C., & Whisler, V. R. (2008). Contextual teaching and learning for practitioners. Journal of Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, 6(4), 54-58.
Hwang, G.-J., & Lai, C.-L. (2017). Facilitating and bridging out-of-class and in-class learning: An interactive e-book-based flipped learning approach for math courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 20(1), 184-197.
Hwang, R.-H., Lin, H.-T., Sun, J. C.-Y., & Wu, J.-J. (2019). Improving learning achievement in science education for elementary school students via blended learning. International Journal of Online Pedagogy and Course Design (IJOPCD), 9(2), 44-62. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJOPCD.2019040104
Isnawan, M. G., Azis, A., & Almazroei, E. E. (2023). Parents’ perspectives on distance learning mathematics during the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study in Indonesia. European Journal of Educational Research, 12(1), 567-581. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.12.1.567
Isnawan, M. G., Suryadi, D., Turmudi, T., & Marfuah, M. (2022). Parental obstacles during distance learning mathematics in Indonesia: A phenomenology study. European Journal of Educational Research, 11(2), 873-883. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.11.2.873
Jamaluddin, M., Mustaji, M., Bachri, B. S., & Sutarto, A. P. (2023). The role of gender and self-efficacy on the relationship between flipped and flex blended learning and mathematics abilities. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 13(5), 873-881. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2023.13.5.1882
Jamaluddin, M., Mustaji, M., & Bahri, B. S. (2022). Effect of blended learning models and self-efficacy on mathematical problem-solving ability. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 21(7), 127-144. https://doi.org/10.26803/ijlter.21.7.7
Jdaitawi, M. (2019). The effect of flipped classroom strategy on students learning outcomes. International Journal of Instruction, 12(3), 665-680. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2019.12340a
Kolomiets, S., Medvedeva, E., & Perevalova, A. (2020). Innovation in teaching multicultural future specialists in Kuzbass coal mining region: A flipped classroom approach In E3S Web of Conferences, (Vol. 174, pp. 04026). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202017404026
Lai, C.-L., & Hwang, G.-J. (2015). An interactive e-book approach to supporting flipped learning in an elementary school math course In 23rd International Conference on Computers in Education, ICCE 2015, Hangzhou (pp. 601-610).
Lai, C.-L., & Hwang, G.-J. (2016). A self-regulated flipped classroom approach to improving students’ learning performance in a mathematics course. Computers & Education, 100, 126-140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.05.006
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2016). A comparison of video production styles in mathematics flipped classroom: Examining students’ preferences In Proceedings of International Conference of the Learning Sciences, ICLS, (Vol. 2, pp. 1282-1285).
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2017). A critical review of flipped classroom challenges in K-12 education: possible solutions and recommendations for future research. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 12(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-016-0044-2
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2017). Using “first principles of instruction” to design mathematics flipped classroom for underperforming students. International journal of learning and teaching, 3(2), 82-89. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijlt.3.2.82-89
Lo, C. K., & Hew, K. F. (2017). Using “first principles of instruction” to design secondary school mathematics flipped classroom: The findings of two exploratory studies. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 20(1), 222-236.
Lo, C. K., Lie, C. W., & Hew, K. F. (2018). Applying “first principles of instruction” as a design theory of the flipped classroom: Findings from a collective study of four secondary school subjects. Computers & Education, 118, 150-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.12.003
Makinde, S. O. (2020). Impact of flipped classroom on mathematics learning outcome of senior secondary school students in Lagos, Nigeria. African Journal of Teacher Education, 9(2), 23-42. https://doi.org/10.21083/ajote.v9i2.6182
Maolidah, I. S., Ruhimat, T., & Dewi, L. (2017). Efektivitas penerapan model pembelajaran flipped classroom pada peningkatan kemampuan berpikir kritis siswa [The effectiveness of implementing the flipped classroom learning model in improving students' critical thinking skills]. Educational Technologia, 3(3), 160-170.
Morse, T. E., Habib, A., Carr, M., & Evans, W. (2022). Flipped classrooms: implications for K-12 students with learning and behavioural challenges from an international exploratory study of teacher educators. Journal of Research in Special Educational Needs, 22(2), 167-174. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-3802.12557
Nadarajan, K., Abdullah, A. H., Alhassora, N. S. A., Ibrahim, N. H., Surif, J., Ali, D. F., Mohd Zaid, N., & Hamzah, M. H. (2023). The effectiveness of a technology-based isometrical transformation flipped classroom learning strategy in improving students’ higher order thinking skills. IEEE Access, 11, 4155-4172. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3230860
Nielsen, K. L. (2020). Students’ video viewing habits during a flipped classroom course in engineering mathematics. Research in Learning Technology, 28, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v28.2404
Nouri, J. (2016). The flipped classroom: for active, effective and increased learning – especially for low achievers. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 13(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-016-0032-z
Nurpratiwi, S., Effendi, M. R., & Amaliyah, A. (2021). Improving religious literacy through Islamic religious education course based on the flipped classroom. Istawa: Jurnal Pendidikan Islam, 6(1), 16-29. https://doi.org/10.24269/ijpi.v6i1.3107
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., & Brennan, S. E. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj, 372(71). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Pattiserlihun, A., & Setiadi, S. J. J. (2020). Blended-flipped classroom learning for physics students with the topic of the photoelectric effect. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan IPA, 6(1), 71-78. https://doi.org/10.21831/jipi.v6i1.28109
Rahmawati, A., & Nuraeni, Z. (2022). Kemandirian belajar siswa melalui pembelajaran flipped classroom pada materi SPLDV kelas VIII berbantuan video animasi [Student learning independence through flipped classroom learning on SPLDV material for class VIII assisted by animated videos]. JURNAL SILOGISME: Kajian Ilmu Matematika dan Pembelajarannya, 6(2), 50-60. https://doi.org/10.24269/silogisme.v6i2.4340
Ramadoni, R., & Chien, K. T. (2023). Integrating peer tutoring video with flipped classroom in online statistics course to improve learning outcomes. Infinity Journal, 12(1), 13-26. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i1.p13-26
Schallert, S. (2021). Towards inquiry-based flipped classroom scenarios in secondary mathematics education: a design-based research study. Dissertation (PhD). Johannes Kepler University linz. Retrieved from https://epub.jku.at/obvulioa/id/6212610
Setiadi, I. (2021). Peningkatan keaktifan dan kemandirian belajar matematika siswa dalam jaringan synchronous menggunakan media crossword puzzle [Increasing students' activeness and independence in learning mathematics in synchronous networks using crossword puzzle media]. Suska Journal of Mathematics Education, 7(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.24014/sjme.v7i1.11938
Sihotang, S. F., Ramadhani, R., Rahim, R., Siregar, R. F., & Ramadhani, R. (2023). Flipped classroom model in mathematics learning: A bibliometric analysis study In The 3rd UPY International Conference on Applied Science and Education (UPINCASE), (Vol. 2491). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0105484
Soebagyo, J., & Saamah, S. (2023). Flipped classroom limited face-to-face learning: A bibliometric study. Al-Ishlah: Jurnal Pendidikan, 15(1), 747-756. https://doi.org/10.35445/alishlah.v15i1.1642
Stöhr, C., & Adawi, T. (2018). Flipped classroom research: From “Black Box” to “White Box” evaluation. Education Sciences, 8(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci8010022
Supra, G. S. R., Munna, N., Oktaviani, E. P., Ardiansyah, A. S., & Asikin, M. (2021). Pengembangan media pembelajaran berbasis gamification dan literasi matematis pada model flipped classroom untuk siswa SMP [Development of learning media based on gamification and mathematical literacy in the flipped classroom model for junior high school students]. In SANTIKA: Seminar Nasional Tadris Matematika, (Vol. 1, pp. 520-548).
Supriyadi, E., Suryadi, D., Turmudi, T., Prabawanto, S., Juandi, D., & Dahlan, J. A. (2023). Didactical design research: A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 18(3), 153-160.
Tekin, O., & Sarıkaya, E. E. (2020). Flipped classroom model in high school mathematics. Bartın University Journal of Faculty of Education, 9(2), 301-314.
Umam, K., Nusantara, T., Parta, I. N., Hidayanto, E., & Mulyono, H. (2019). An application of flipped classroom in mathematics teacher education programme. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 13(3), 68-79. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v13i03.10207
Urquiza-Fuentes, J. (2020). Increasing students’ responsibility and learning outcomes using partial flipped classroom in a language processors course. IEEE Access, 8, 211211-211223. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039628
Wan, R., Li, L., Xing, C., Peng, R., & Gao, L. (2019). Worldwide scientific productions with immunotherapy of sepsis: a bibliometric analysis. PeerJ, 7, e7116. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7116
Yanuarto, W. N. (2018). The flipped classroom learning model untuk menumbuhkan kemandirian belajar matematika dan memaksimalkan peran teknologi pada pendidikan [The flipped classroom learning model to foster independence in learning mathematics and maximize the role of technology in education]. De Fermat: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 1(1), 13-19. https://doi.org/10.36277/defermat.v1i1.10
Yarbro, J., Arfstrom, K. M., McKnight, K., & McKnight, P. (2014). Extension of a review of flipped learning. George Mason University. Retrieved from https://www.lifelongfaith.com/uploads/5/1/6/4/5164069/review_of_flipped_learning.pdf
Ying, Y. S., & Mohd Ayub, A. F. (2022). The impact of flipped classroom instructional model in teaching English as a second language (ESL) among lower secondary pupils. International Journal of Education, 14(4), 15-32. https://doi.org/10.5296/ije.v14i4.20559
Zhang, D., Zhao, J. L., Zhou, L., & Nunamaker, J. F. (2004). Can e-learning replace classroom learning? Commun. ACM, 47(5), 75–79. https://doi.org/10.1145/986213.986216