The effect of teaching props on the mathematical problem-solving skills: A meta-analysis study
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
Abstract
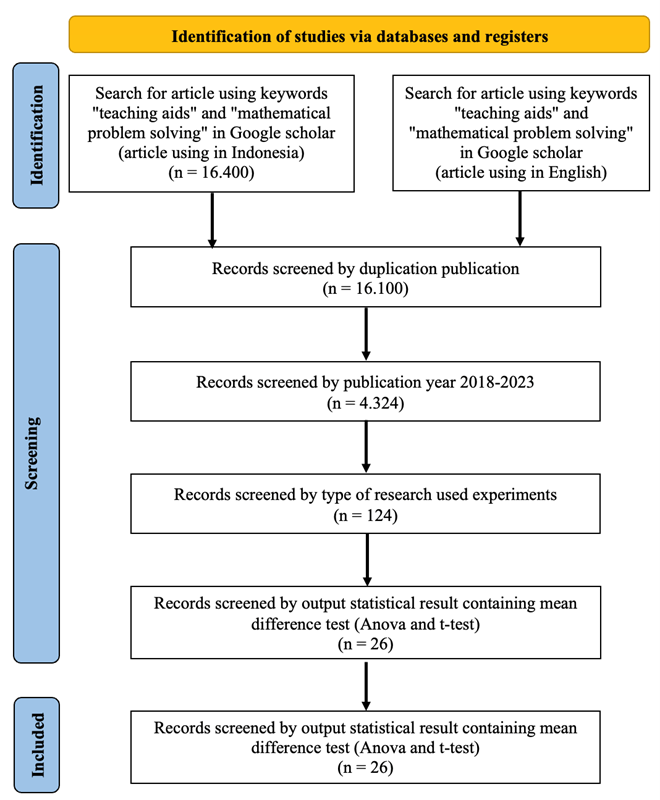
Researchers have widely researched the effects of teaching props, and most concluded that, statistically, there is an effect on problem-solving ability. However, how significant is the effect on problem-solving ability, and whether their research results are parallel to other research they have yet to do? So, the reliability of research related to teaching props still needs to be considered. This research aims to analyze the results that examine teaching props on problem-solving abilities. The method used in this research is meta-analysis. This research was carried out through meta-analysis stages, namely determining inclusion criteria, collecting data and coding variables, statistical analysis by determining the effect size, and making conclusions from the data obtained. Data collection was carried out by collecting data from research conducted from 2018 to 2023 on the Google Scholar database. This data collection obtained twenty-six (26) studies that met the inclusion criteria for extraction from research and development, experimental, and quasi-experimental. Effect size measures the effect of teaching props on students' problem-solving abilities. Based on these calculations, an effect size value of 2.449. This research indicates a significant and positive influence between teaching props and students' problem-solving skills, especially in mathematical learning. Therefore, it is necessary to develop teaching props to improve mathematical problem-solving skills.
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The author is responsible for acquiring the permission(s) to reproduce any copyrighted figures, tables, data, or text that are being used in the submitted paper. Authors should note that text quotations of more than 250 words from a published or copyrighted work will require grant of permission from the original publisher to reprint. The written permission letter(s) must be submitted together with the manuscript.References
Afgani, M. W., & Paradesa, R. (2021). Pisa-like problems using islamic ethnomathematics approach. Infinity Journal, 10(2), 203-216. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v10i2.p203-216
Aisyah, N., Susanti, E., Meryansumayeka, Siswono, T. Y. E., & Maat, S. M. (2023). Proving geometry theorems: Student prospective teachers’ perseverance and mathematical reasoning. Infinity Journal, 12(2), 377-392. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i2.p377-392
Akben, N. (2020). Effects of the problem-posing approach on students’ problem solving skills and metacognitive awareness in science education. Research in Science Education, 50(3), 1143-1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-018-9726-7
Albab, R. U., Wanabuliandari, S., & Sumaji, S. (2021). Pengaruh model problem based learning berbantuan aplikasi Gagung Duran terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah siswa [The influence of the problem-based learning model assisted by the Gagung Duran application on students' problem-solving abilities]. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 10(3), 1767-1767. https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v10i3.3969
Ali, G., Haolader, F. A., & Muhammad, K. (2013). The role of ICT to make teaching-learning effective in higher institutions of learning in Uganda. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 2(8), 4061-4073.
Ambarita, S. M., Asri, L., Agustina, A., Octavianty, D., & Zulkardi, Z. (2018). Mathematical modeling skills on solving PISA problems. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1097(1), 012115. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1097/1/012115
Anggraeni, D. R., Bintoro, H. S., & Rahayu, R. (2022). Efektivitas model accelerated-problem based learning berbantuan aplikasi bangun ruang (Abaru) untuk meningkatkan kemampuan pemecahan masalah dan disposisi matematis siswa [The effectiveness of the accelerated problem-based learning model assisted by the spatial geometry application (Abaru) to improve students' problem-solving abilities and mathematical dispositions]. In (Vol. 1, pp. 87-101).
Aravantinos, S., Lavidas, K., Voulgari, I., Papadakis, S., Karalis, T., & Komis, V. (2024). Educational approaches with AΙ in primary school settings: A systematic review of the literature available in scopus. Education Sciences, 14(7), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14070744
Arbo, J. B., & Ching, D. A. (2022). Problem-based learning approach in developing mathematical skills. International Journal of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics, 2(1), 26-47. https://doi.org/10.53378/352873
Asiyai, R. I. (2015). Improving quality higher education in Nigeria: The roles of stakeholders. International Journal of Higher Education, 4(1), 61-70. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v4n1p61
Astuti, A., Oktaviana, D., & Firdaus, M. (2022). Pengaruh media pembelajaran quizizz terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis dan kemandirian belajar pada siswa SMP [The Influence of quizizz learning media on mathematical problem-solving skills and learning independence in junior high school students]. Media Pendidikan Matematika, 10(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.33394/mpm.v10i1.5039
Attami, D., Budiyono, B., & Indriati, D. (2020). The mathematical problem-solving ability of junior high school students based on their mathematical resilience. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1469(1), 012152. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1469/1/012152
Attard, C., & Holmes, K. (2020). “It gives you that sense of hope”: An exploration of technology use to mediate student engagement with mathematics. Heliyon, 6(1), e02945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02945
Avvisati, F., & Borgonovi, F. (2020). Learning mathematics problem solving through test practice: A randomized field experiment on a global scale. Educational Psychology Review, 32(3), 791-814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09520-6
Azizah, T., Fauzan, A., & Harisman, Y. (2022). "Flipped classroom type peer instruction-based learning" based on a website to improve student's problem solving. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 325-348. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p325-348
Berutu, R., Saputra, E., & Aklimawati, A. (2022). Pengaruh model pembelajaran missouri mathematics project (MMP) berbantuan alat peraga terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis siswa di kelas XI SMA negeri 1 Gunung Meriah [The influence of the Missouri Mathematics Project (MMP) learning model assisted by teaching aids on students' mathematical problem solving abilities in class XI of SMA Negeri 1 Gunung Meriah]. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Malikussaleh, 2(1), 181-190. https://doi.org/10.29103/jpmm.v2i1.7369
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470743386
Chidyaka, C., & Nkhata, B. (2019). Metacognition strategies in solving mathematics at a secondary school in Zambia. Journal of Education and Practice, 10(15), 118-134. https://doi.org/10.7176/jep/10-15-15
Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2012). Meta-analysis, review and update of methodologies. In Statistics applied to clinical studies (pp. 379-390). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2863-9_33
Cooper, H., Hedges, L. V., & Valentine, J. C. (2019). The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis (3rd ed.). Russell Sage Foundation.
Cuevas, J. (2015). Is learning styles-based instruction effective? A comprehensive analysis of recent research on learning styles. Theory and Research in Education, 13(3), 308-333. https://doi.org/10.1177/1477878515606621
Cumming, G. (2013). Understanding the new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203807002
Devita, D., Hardianti, D., Desmayanasari, D., Hesti, H., Lestari, F., Noprisa, N., & Marhani, M. (2023). Analysis of mathematics learning on mild intellectual disabilities students in special school. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2727(1), 020046. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0141802
Dinçer, S. (2018). Content analysis in scientific research: Meta-analysis, meta-synthesis, and descriptive content analysis. Bartın Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 7(1), 176-190. https://doi.org/10.14686/buefad.363159
Ekowati, V. I., Nurhayati, E., Suwarna, S., & Saputri, I. I. (2023). Program for international student assessment-based analysis for Javanese test. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 12(2), 1122-1135. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v12i2.24426
Erbilgin, E., & Macur, G. M. A. (2022). A subtraction game to scaffold primary students’ word problem solving skills. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(2), 307-322. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i2.pp307-322
Fadlilah, M. F., Purwanto, S., & El Hakim, L. (2021). Pengaruh model pembelajaran team assisted individualization (TAI) berbatuan video interaktif dalam pembelajaran jarak jauh terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis siswa SMP negeri 172 Jakarta [The influence of the team-assisted individualization (TAI) learning model using interactive videos in distance learning on the mathematical problem-solving abilities of students at SMP Negeri 172 Jakarta]. Jurnal Riset Pembelajaran Matematika Sekolah, 5(2), 14-26. https://doi.org/10.21009/jrpms.052.02
Ferguson, C. J. (2016). An effect size primer: A guide for clinicians and researchers. In A. E. Kazdin (Ed.), Methodological issues and strategies in clinical research (4th ed., pp. 301-310). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/14805-020
Gurevitch, J., Koricheva, J., Nakagawa, S., & Stewart, G. (2018). Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature, 555(7695), 175-182. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25753
Hadi, S., Retnawati, H., Munadi, S., Apino, E., & Wulandari, N. F. (2018). The difficulties of high school students in solving higher-order thinking skills problems. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 76(4), 520-532. https://doi.org/10.33225/pec/18.76.520
Hakim, L. L., Alghadari, F., & Widodo, S. A. (2019). Virtual manipulatives media in mathematical abstraction. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1315(1), 012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1315/1/012017
Handayani, T., Sutiarso, S., & Firdaus, R. (2023). Pengaruh media pembelajaran berbasis flipaclip terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis dan kemandirian belajar siswa [The influence of flipaclip-based learning media on students' mathematical problem-solving abilities and learning independence]. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 7(1), 350-366. http://journal.stkip-andi-matappa.ac.id/index.php/histogram/index
Hanifah, H., Supriadi, N., & Widyastuti, R. (2019). Pengaruh model pembelajaran e-learning berbantuan media pembelajaran edmodo terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis peserta didik [The influence of the e-learning learning model assisted by Edmodo learning media on students' mathematical problem solving abilities]. Numerical: Jurnal Matematika dan Pendidikan Matematika, 3(1), 31-42. https://doi.org/10.25217/numerical.v3i1.453
Harefa, D., & La'ia, H. T. (2021). Media pembelajaran audio video terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika siswa [Audio video learning media on students' mathematical problem solving abilities]. Aksara: Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan Nonformal, 7(2), 327-338. https://doi.org/10.37905/aksara.7.2.327-338.2021
Harisman, Y., Noto, M. S., & Hidayat, W. (2020). Experience student background and their behavior in problem solving. Infinity Journal, 9(1), 59-68. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v9i1.p59-68
Hasibuan, A. M., Saragih, S., & Amry, Z. (2019). Development of learning materials based on realistic mathematics education to improve problem solving ability and student learning independence. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 243-252. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/4000
Hasibuan, L. R., Siregar, S. U., Juliyanti, E., & Nasution, M. (2020). Pengaruh penerapan model kooperatif learning tipe TAPPS menggunakan alat peraga terpisah dan tipe TPS terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika kelas X materi ruang dimensi tiga di SMAN 2 Rantau Selatan [The effect of implementing the TAPPS type cooperative learning model using separate teaching aids and the TPS type on the mathematical problem-solving abilities of class X students on three-dimensional space material at SMAN 2 Rantau Selatan]. Jurnal Pembelajaran dan Matematika Sigma (JPMS), 6(1), 36-40. https://doi.org/10.36987/jpms.v6i1.1672
Hasyanah, Y., Sukmaningthias, N., Sari, N., & Nuraeni, Z. (2023). Pengaruh digital komik berbasis realistic mathematic education terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah [The influence of digital comics based on realistic mathematical education on problem-solving skills]. JTMT: Journal Tadris Matematika, 4(1), 56-65.
Hedges, L. V., & Olkin, I. (2014). Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Academic press.
Hendikawati, P., Zahid, M. Z., & Arifudin, R. (2019). Keefektifitas media pembelajaran berbasis android terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah dan kemandirian belajar [The effectiveness of Android-based learning media on problem-solving skills and learning independence]. In PRISMA, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Matematika, (Vol. 2, pp. 917-927).
Hendriana, H., Johanto, T., & Sumarmo, U. (2018). The role of problem-based learning to improve students' mathematical problem-solving ability and self confidence. Journal on Mathematics Education, 9(2), 291-300. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.9.2.5394.291-300
Hesse, F., Care, E., Buder, J., Sassenberg, K., & Griffin, P. (2015). A framework for teachable collaborative problem solving skills. In P. Griffin & E. Care (Eds.), Assessment and teaching of 21st century skills: Methods and approach (pp. 37-56). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9395-7_2
Hikmah, N. (2018). Pengaruh model pembelajaran matematika, media jaring-jaring terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah [The influence of mathematics learning models, net media on problem solving abilities]. JKPM (Jurnal Kajian Pendidikan Matematika), 4(1), 61-66. https://doi.org/10.30998/jkpm.v4i1.3063
Huinker, D., Bush, S. B., & Graham, K. J. (2020). Catalyzing change in school mathematics: Creating the opportunities our students deserve. Mathematics Teacher: Learning and Teaching PK-12, 113(10), 780-790. https://doi.org/10.5951/mtlt.2020.0053
Hutajulu, M., Perbowo, K. S., Alghadari, F., Minarti, E. D., & Hidayat, W. (2022). The process of conceptualization in solving geometric-function problems. Infinity Journal, 11(1), 145-162. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i1.p145-162
Ibrahim, I., & Widodo, S. A. (2020). Advocacy approach with open-ended problems to mathematical creative thinking ability. Infinity Journal, 9(1), 93-102. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v9i1.p93-102
Ismawati, E., Hersulastuti, H., Amertawengrum, I. P., & Anindita, K. A. (2023). Portrait of education in Indonesia: learning from PISA results 2015 to present. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 22(1), 321-340. https://doi.org/10.26803/ijlter.22.1.18
Joan, D. R. R. (2015). An introduction to various types of mathematics teaching aids. i-manager’s Journal on Mathematics, 4(2), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.26634/jmat.4.2.3496
Juliantini, L. S., Jampel, I. N., & Diputra, K. S. (2020). Pengaruh model pembelajaran brain based learning berbantuan media konkret terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika siswa kelas IV SD [The influence of the brain based learning model assisted by concrete media on the mathematical problem solving abilities of grade IV elementary school students]. Thinking Skills and Creativity Journal, 3(1), 8-17. https://doi.org/10.23887/tscj.v3i1.24304
Kamaliyah, K., Zulkardi, Z., & Darmawijoyo, D. (2013). Developing the sixth level of PISA-like mathematics problems for secondary school students. Journal on Mathematics Education, 4(1), 9-28. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.4.1.559.9-28
Kartianom, K., & Ndayizeye, O. (2017). What ‘s wrong with the Asian and African students’ mathematics learning achievement? The multilevel PISA 2015 data analysis for Indonesia, Japan, and Algeria. Jurnal Riset Pendidikan Matematika, 4(2), 200-210. https://doi.org/10.21831/jrpm.v4i2.16931
Kartianom, K., & Retnawati, H. (2018). Why are their mathematical learning achievements different? Re-analysis TIMSS 2015 data in Indonesia, Japan and Turkey. International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their Implications, 9(2), 33-46.
Košir, K., & Tement, S. (2014). Teacher–student relationship and academic achievement: a cross-lagged longitudinal study on three different age groups. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 29(3), 409-428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-013-0205-2
Kurniansyah, M. Y., Hidayat, W., & Rohaeti, E. E. (2022). Development of combined module using contextual scientific approach to enhance students' cognitive and affective. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 349-366. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p349-366
Kusmaryono, I., & Kusumaningsih, W. (2023). Evaluating the results of PISA assessment: are there gaps between the teaching of mathematical literacy at schools and in PISA assessment? European Journal of Educational Research, 12(3), 1479-1493. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.12.3.1479
Kusumadewi, C. A., & Retnawati, H. (2020). Identification of elementary school students’ difficulties in mathematical problem-solving. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1511(1), 012031. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1511/1/012031
Kwak, S. G., & Kim, J. H. (2017). Central limit theorem: The cornerstone of modern statistics. Korean journal of anesthesiology, 70(2), 144-156. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2017.70.2.144
Lakens, D. (2022). Sample size justification. Collabra: Psychology, 8(1), 33267. https://doi.org/10.1525/collabra.33267
Larbi, E., & Mavis, O. (2016). The use of manipulatives in mathematics education. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(36), 53-61. www.iiste.org
Lee, L.-K., Chau, C.-H., Chau, C.-H., Ng, C.-T., Hu, J.-H., Wong, C.-Y., Yu, L.-C., & Wu, N.-I. (2019). Improving the experience of teaching and learning kindergarten-level English vocabulary using augmented reality. International Journal of Innovation and Learning, 25(2), 110-125. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJIL.2019.097661
Leung, A., & Bolite-Frant, J. (2015). Designing mathematics tasks: The role of tools. In A. Watson & M. Ohtani (Eds.), Task design in mathematics education: an ICMI study 22 (pp. 191-225). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09629-2_6
Maulidia, F., Johar, R., & Andariah. (2019). A case study of students’ creativity in solving mathematical problems through problem based learning. Infinity Journal, 8(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v8i1.p1-10
McShane, B. B., & Böckenholt, U. (2017). Single-paper meta-analysis: Benefits for study summary, theory testing, and replicability. Journal of Consumer Research, 43(6), 1048-1063. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucw085
Meutia, C. I., Ikhsan, M., & Saminan, S. (2020). Mathematical problem-solving skills of junior high school students. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1460(1), 012010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1460/1/012010
Modebelu, M. N., & Duvie, A. N. (2012). Innovative methods and strategies for effective teaching and learning. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 3(13), 145-154.
Mudaly, V., & Naidoo, J. (2015). The concrete-representational-abstract sequence of instruction in mathematics classrooms. Perspectives in Education, 33(1), 42-56. https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC168542
Mulqueeny, K., Kostyuk, V., Baker, R. S., & Ocumpaugh, J. (2015). Incorporating effective e-learning principles to improve student engagement in middle-school mathematics. International journal of STEM education, 2(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-015-0028-6
Mulyani, A. H., Suryaningrat, E. F., Pujiasti, D. A., & Mutaqin, E. J. (2022). Pengaruh media smart book terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika [The influence of smart book media on mathematical problem-solving abilities]. caXra: Jurnal Pendidikan Sekolah Dasar, 2(2), 106-115. https://doi.org/10.31980/caxra.v2i2.849
Murtafiah, W., Lestari, N. D. S., Yahya, F. H., Apriandi, D., & Suprapto, E. (2023). How do students' decision-making ability in solving open-ended problems? Infinity Journal, 12(1), 133-150. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v12i1.p133-150
Murtafiah, W., Wardani, Y. N., Darmadi, D., & Widodo, S. A. (2024). Profile of open-start problem-solving with context Sarangan Lake viewed students' learning styles in junior high school. Journal of Education and Learning, 18(2), 448-461. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v18i2.21051
National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. (2020). Principles and standards for school mathematics. NCTM.
Ningrum, A., Astuti, Y., Kusumaningrum, B., Widodo, S. A., Asmarani, N., Dewi, K., & Irfan, M. (2023). The creativity of mentally retarded students in solving plane problems with image media. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan MIPA, 13(2), 151-166. https://doi.org/10.30998/formatif.v13i2.16177
Niu, S. J., Niemi, H., & Furman, B. (2022). Supporting K-12 students to learn social-emotional and self-management skills for their sustainable growth with the solution-focused kids’ skills method. Sustainability, 14(13), 7947. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137947
Noviatika, R., Gunawan, G., & Rokhmat, J. (2019). Pengaruh model pembelajaran berbasis masalah berbantuan mobile pocket book fisika terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah peserta didik [The influence of problem-based learning models assisted by mobile pocket books in physics on students' problem-solving abilities]. Jurnal Pendidikan Fisika dan Teknologi, 5(2), 240-246. https://doi.org/10.29303/jpft.v5i2.1163
Nugrahanto, S., & Zuchdi, D. (2019). Indonesia PISA result and impact on the reading learning program in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Interdisciplinary Language, Literature and Education (ICILLE 2018), (pp. 373-377). https://doi.org/10.2991/icille-18.2019.77
OECD. (2019). PISA 2018 Results: Combined Executive Summaries, Volume I, II & III. OECD Publishing.
OECD. (2023). PISA 2022 Results (Volume I): The State of Learning and Equity in Education. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/53f23881-en
Olivares, D., Lupiáñez, J. L., & Segovia, I. (2021). Roles and characteristics of problem solving in the mathematics curriculum: a review. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 52(7), 1079-1096. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2020.1738579
Osana, H. P., & Duponsel, N. (2016). Manipulatives, diagrams, and mathematics: A framework for future research on virtual manipulatives. In P. S. Moyer-Packenham (Ed.), International perspectives on teaching and learning mathematics with virtual manipulatives (pp. 95-120). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32718-1_5
Özreçberoğlu, N., & Çağanağa, Ç. K. (2018). Making it count: Strategies for improving problem-solving skills in mathematics for students and teachers' classroom management. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(4), 1253-1261. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/82536
Partayasa, W., Suharta, I. G. P., & Suparta, I. N. (2020). Pengaruh model creative problem solving (CPS) berbantuan video pembelajaran terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah ditinjau dari minat [The influence of the creative problem solving (CPS) model assisted by learning videos on problem solving abilities viewed from the perspective of interest]. JNPM (Jurnal Nasional Pendidikan Matematika), 4(1), 168-168. https://doi.org/10.33603/jnpm.v4i1.2644
Pigott, T., & Moon, S. M. (2016). Introduction to the meta-analysis special issue. Gifted Child Quarterly, 60(2), 79-80. https://doi.org/10.1177/0016986216634439
Piñeiro, J. L., Castro-Rodríguez, E., & Castro, E. (2022). What problem-solving knowledge is required in mathematical teaching? A curricular approach. Curriculum Perspectives, 42(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41297-021-00152-6
Polya, G. (2014). How to solve it: A new aspect of mathematical method (Vol. 34). Princeton university press.
Powell, E. (2021). Innovative instructional methods integrating 21st-century competencies in mathematics education: Communication, collaboration, critical thinking, creativity. In H. K. Dhir (Ed.), Handbook of research on barriers for teaching 21st-century competencies and the impact of digitalization (pp. 234-252). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-6967-2.ch013
Praekhaow, P., Chindanurak, T., Konglok, S. A., & Sokhuma, K. (2021). Studying conditions and problems for developing mathematics learning model of undergraduate students in Thailand. Infinity Journal, 10(1), 121-132. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v10i1.p121-132
Pramuditya, S. A., Noto, M. S., & Azzumar, F. (2022). Characteristics of students' mathematical problem solving abilities in open-ended-based virtual reality game learning. Infinity Journal, 11(2), 255-272. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i2.p255-272
Pratidiana, D., Pujiastuti, H., & Santosa, C. A. H. F. (2022). Pengaruh model pembelajaran flipped classroom dan gaya kognitif terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematis siswa [The influence of the flipped classroom learning model and cognitive style on students' mathematical problem-solving abilities]. MENDIDIK: Jurnal Kajian Pendidikan dan Pengajaran, 8(2), 206-215. https://doi.org/10.30653/003.202282.233
Puspitasari, L., In'am, A., & Syaifuddin, M. (2018). Analysis of students’ creative thinking in solving arithmetic problems. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(1), 49-60. https://doi.org/10.12973/iejme/3962
Pusporini, W., Widodo, S. A., Wijayanti, A., Wijayanti, N., Utami, W. B., Taqiyudin, M., & Irfan, M. (2023). Mathematical knowledge content in junior high school curriculum: A comparative study of the 2013 curriculum and merdeka curriculum. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 12(2), 389-404. https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v12i2.795
Putri, E. M. E., & Putra, L. V. (2021). Keefektifan model pembelajaran two stay two stray berbantuan alat peraga bangun datar untuk meningkatkan kemampuan pemecahan masalah siswa kelas IV SD negeri Madyocondro [The effectiveness of the two stay two stray learning model assisted by flat geometric props to improve the problem-solving abilities of fourth grade students at Madyocondro state elementary School]. Jurnal Perseda, 4(2), 128-133. https://doi.org/10.37150/perseda.v4i2.1288
Putri, R. I. I., Zulkardi, Z., & Riskanita, A. D. (2022). Students’ problem-solving ability in solving algebra tasks using the context of Palembang. Journal on Mathematics Education, 13(3), 549-564. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.v13i3.pp549-564
Rahmadani, E., & Sumardi, H. (2019). Peningkatan kemampuan pemecahan masalah siswa menggunakan pendekatan matematika realistik berbantuan alat peraga klinometer [Improving students' problem-solving abilities using a realistic mathematics approach assisted by clinometer teaching aids]. Jurnal MathEducation Nusantara, 2(2), 143-149.
Rasmitadila, R., Widyasari, W., Prasetyo, T., Rachmadtullah, R., Samsudin, A., & Aliyyah, R. R. (2021). General teachers’ experience of the Brain’s natural learning systems-based instructional approach in inclusive classroom. International Journal of Instruction, 14(3), 95-116. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2021.1436a
Safitri, W. C. D. (2019). Efektivitas media board game terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah pada pembelajaran tematik di SD [The effectiveness of board game media on problem-solving skills in thematic learning in elementary schools]. Mimbar PGSD Undiksha, 7(2), 72-78.
Saidek, A. R., Islami, R., & Abdoludin, A. (2016). Character issues: Reality character problems and solutions through education in Indonesia. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(17), 158-165.
Sari, P. C., Eriani, N. D., Audina, T., & Setiawan, W. (2019). Pengaruh pembelajaran berbantuan geogebra terhadap peningkatan kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematik siswa smp [The effect of Geogebra-assisted learning on improving junior high school students' mathematical problem-solving abilities]. Journal on Education, 1(3), 411-416.
Sari, R. Y., Saputra, H. J., & Azizah, M. (2019). Penerapan model numbered heads together berbantu dakonmatika pada kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika [Application of the numbered heads together model assisted by Dakonmatika on mathematical problem-solving abilities]. Jurnal Ilmiah Sekolah Dasar, 3(1), 51-56. https://doi.org/10.23887/jisd.v3i1.17180
Schoenfeld, A. H. (2014). Mathematical problem solving. Elsevier.
Septiani, Y. D., Lubis, P., & Ratnaningdyah, D. (2020). Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Guided Inquiry Berbantuan Alat Peraga Terhadap Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Siswa Sma [The influence of guided inquiry learning model assisted by teaching aids on problem-solving ability of high school students]. Jurnal Luminous: Riset Ilmiah Pendidikan Fisika, 1(1), 45-45. https://doi.org/10.31851/luminous.v1i1.3446
Setiawan, Y. E. (2022). Prospective teachers representations in problem solving of special angle trigonometry functions based on the level of ability. Infinity Journal, 11(1), 55-76. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i1.p55-76
Siagian, M. V., Saragih, S., & Sinaga, B. (2019). Development of learning materials oriented on problem-based learning model to improve students’ mathematical problem solving ability and metacognition ability. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(2), 331-340. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/5717
Stacey, K., & Turner, R. (2015). The evolution and key concepts of the PISA mathematics frameworks. In K. Stacey & R. Turner (Eds.), Assessing mathematical literacy: The PISA experience (pp. 5-33). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10121-7_1
Sternad, D. (2021). Solve it!: The mindset and tools of smart problem solvers. Econcise.
Steyn, G., & Adendorff, S. A. (2020). Questioning techniques used by foundation phase education students teaching mathematical problem-solving. South African Journal of Childhood Education, 10(1), a564. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajce.v10i1.564
Sugiman, S., Pujiastuti, E., & Lestari, S. D. (2021). Increasing of the blind students’ mathematical imagination through inquiry-based learning assisted with manipulative props. Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry, 12(9), 1422-1437. https://www.tojqi.net/index.php/journal/article/view/5879
Tristanti, L. B., Akbar, S., & Rahayu, W. A. (2021). Pengaruh media pembelajaran game edukasi berbasis construct terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah dan hasil belajar siswa [The influence of construct-based educational game learning media on students' problem-solving abilities and learning outcomes]. Mosharafa: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 10(1), 129-140. https://doi.org/10.31980/mosharafa.v10i1.647
Tülübaş, T., Karakose, T., & Papadakis, S. (2023). A holistic investigation of the relationship between digital addiction and academic achievement among students. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 13(10), 2006-2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13100143
Tuong, H. A., Nam, P. S., Hau, N. H., Tien, V. T. B., Lavicza, Z., & Hougton, T. (2023). Utilizing STEM-based practices to enhance mathematics teaching in Vietnam: Developing students' real-world problem solving and 21st century skills. Journal of Technology and Science Education, 13(1), 73-91. https://doi.org/10.3926/jotse.1790
Ulandari, L., Amry, Z., & Saragih, S. (2019). Development of learning materials based on realistic mathematics education approach to improve students’ mathematical problem solving ability and self-efficacy. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 14(2), 375-383. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/5721
Utami, W. B., Aulia, F., Permatasari, D., Taqiyuddin, M., & Widodo, S. A. (2022). Ketupat Eid tradition of the north coast of Java as an alternative mathematics learning media. Infinity Journal, 11(1), 177-192. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v11i1.p177-192
van Aken, J., & Berends, H. (2012). Problem solving in organizations: A methodological handbook for business and management students. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9781139094351
van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2013). Perspectives on problem solving and instruction. Computers & Education, 64, 153-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.11.025
Verawati, A., Agustito, D., Pusporini, W., Utami, W. B., & Widodo, S. A. (2022). Designing android learning media to improve problem-solving skills of ratio. Advances in Mobile Learning Educational Research, 2(1), 216-224. https://doi.org/10.25082/amler.2022.01.005
Weinhandl, R., & Lavicza, Z. (2021). Real-world modelling to increase mathematical creativity. Journal of Humanistic Mathematics, 11(1), 265-299. https://doi.org/10.5642/jhummath.202101.13
Widodo, S. A., Turmudi, T., & Dahlan, J. A. (2019). An error students in mathematical problems solves based on cognitive development. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 8(7), 433-439.
Widodo, S. A., Wijayanti, A., Irfan, M., Pusporini, W., Mariah, S., & Rochmiyati, S. (2023). Effects of worksheets on problem-solving skills: Meta-analytic studies. International Journal of Educational Methodology, 9(1), 151-167. https://doi.org/10.12973/ijem.9.1.151
Wijaya, T. T., Cao, Y., Weinhandl, R., & Tamur, M. (2022). A meta-analysis of the effects of e-books on students' mathematics achievement. Heliyon, 8(6), e09432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09432
Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
Wijayanti, A., Widodo, S. A., Pusporini, W., Wijayanti, N., Irfan, M., & Trisniawati, T. (2022). Optimization of mathematics learning with problem based learning and 3N (niteni, nirokke, nambahi) to improve mathematical problem solving skills. IndoMath: Indonesia Mathematics Education, 5(2), 123-134.
Yu, K.-C., Fan, S.-C., & Lin, K.-Y. (2015). Enhancing students’ problem-solving skills through context-based learning. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 13(6), 1377-1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-014-9567-4
Yuliana, F., Leto, K. T., & Ndori, V. H. (2022). Pengaruh penggunaan video pembelajaran terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah kimia peserta didik kelas X di SMA negeri 1 Nita [The effect of using learning videos on the chemistry problem solving abilities of class X students at SMA Negeri 1 Nita]. Dalton : Jurnal Pendidikan Kimia dan Ilmu Kimia, 5(2), 22-29.
Zulkarnaen, R., & Kusumah, Y. S. (2019). Students’ mathematical modeling abilities in interpretation-construction design model. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1318(1), 012097. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1318/1/012097